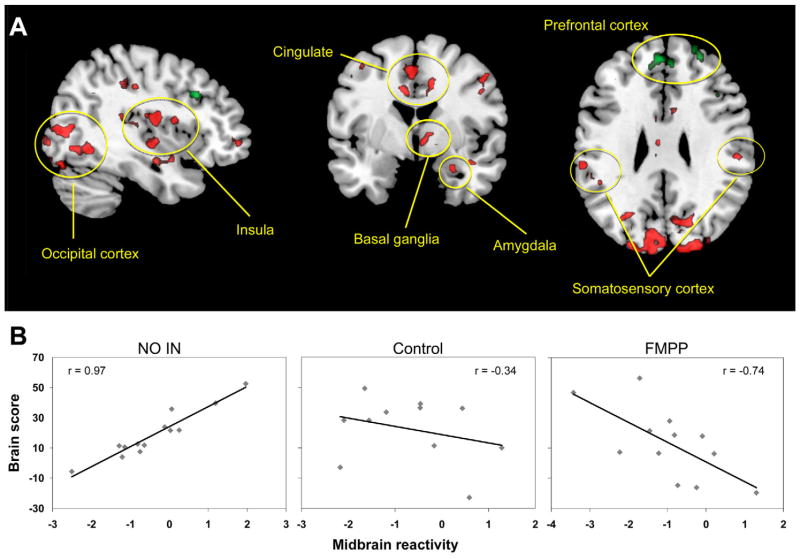
Figure 3.
A resting-state midbrain centered network has strong positive correlation with midbrain emotional reactivity after No-Intervention, is not engaged after Control, and is negatively correlated with midbrain activity after FMPP. This suggests a shift away from an arousal-based resting-state network and toward a regulatory network. Network regions are depicted in (A) (detailed in Supplementary Tables 4A and B). Red regions show areas that are positively correlated with midbrain activity in the No-Intervention group and negatively correlated in the FMPP group. Green regions are negatively correlated with midbrain activity in the No-Intervention group and are positively correlated in the FMPP group. (B) Correlation of the network with midbrain reactivity by group.