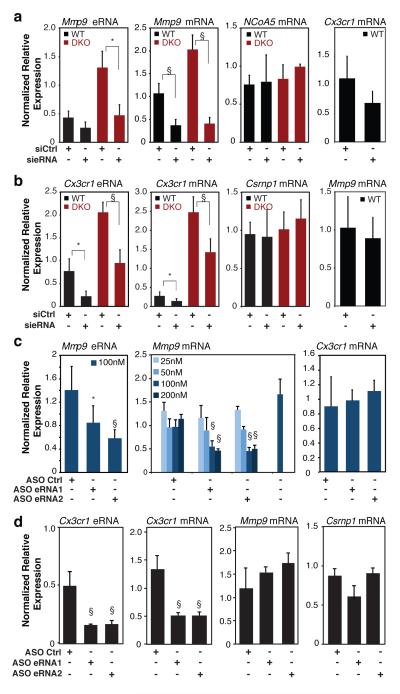
Figure 3. Reduction of eRNA expression results in reduced expression of nearby mRNAs.
a, Q-PCR analysis of Mmp9 eRNA, and Mmp9, NCoA5 and Cx3cr1 mRNAs for wildtype and Rev-Erb DKO thioglycollate-elicited macrophages transfected with Ctrl or Mmp9 eRNA siRNA (N WT = 4, and N DKO = 4). b, Q-PCR analysis of Cx3cr1 eRNA, and Cx3cr1, Csrnp1 and Mmp9 mRNAs for wildtype and Rev-Erb DKO bone marrow-derived macrophages transfected with siRNA targeting Cx3cr1 eRNA (N WT = 6, and N DKO = 5). c, Q-PCR analysis of Mmp9 eRNA and Mmp9 and Cx3cr1 mRNAs in thioglycollate-elicited macrophages transfected with the indicated antisense oligonucleotides (ASO, n = 3-7 per condition). d, Q-PCR analysis of Cx3cr1 eRNA and Cx3cr1, Mmp9 and Csrnpl mRNAs in BMDMs transfected with the indicated antisense oligonucleotides (ASO, n = 3-7 per condition). Data in a-d represent mean + s.d., with expression normalized to 36B4 in all cases. For a-b, statistical significance was determined by two tails Student’s t-test; for c-d, one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD test. P value, * P < 0.05, § P < 0.005 versus control.