Figure 1. HLA-A2-specific binding affinity and stability of XBP1 US, XBP1 SP, CD138, and CS1 multipeptide.
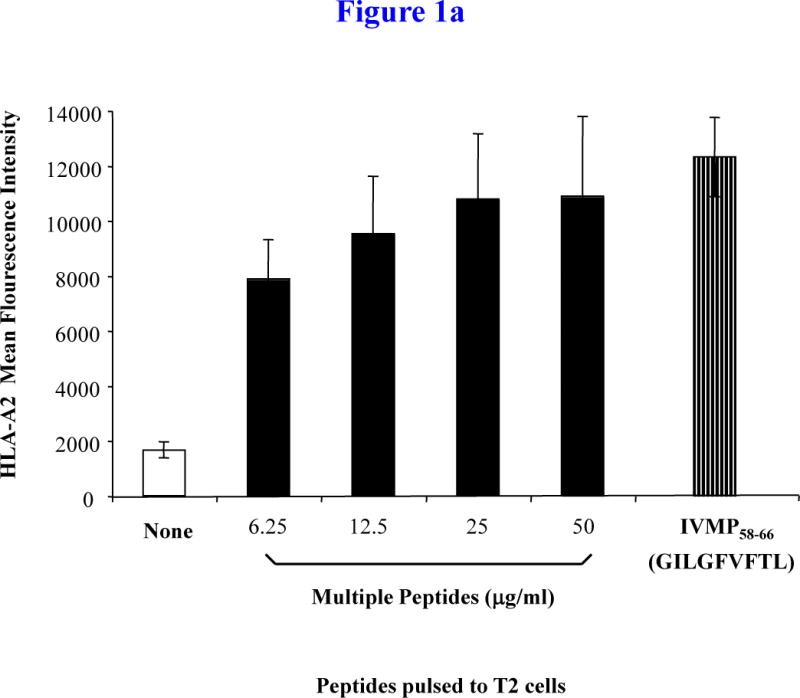
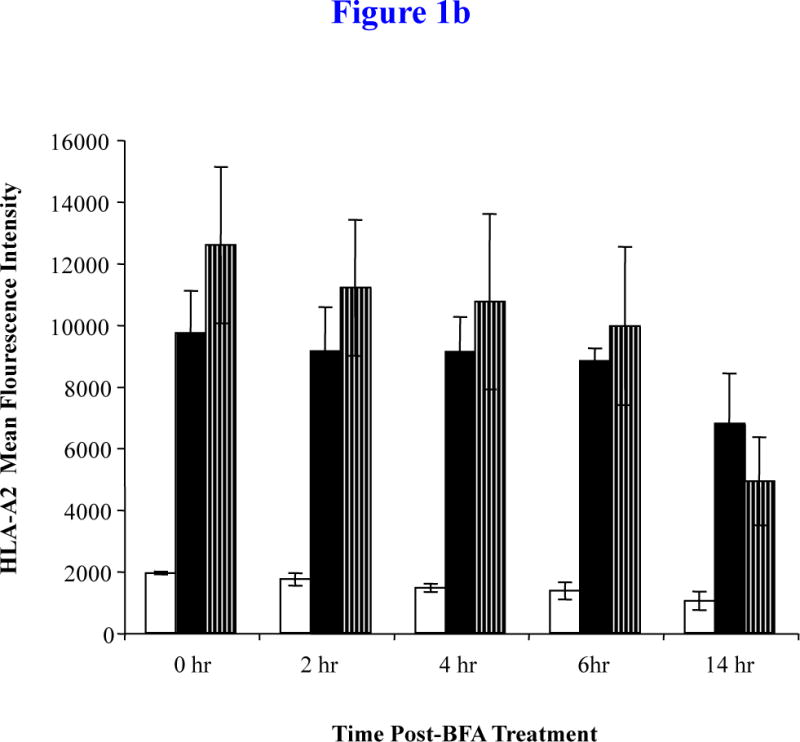
Figure 1a. HLA-A2 binding capacity of multipeptide (MP) cocktail
T2 cells were pulsed overnight with a cocktail of heteroclitic XBP1 US184–192 (YISPWILAV), heteroclitic XBP1 SP367–375 (YLFPQLISV), native CD138260–268 (GLVGLIFAV) and native CS1239–247 (SLFVLGLFL) peptides in serum-fee AIM-V media at total peptide concentrations ranging from 0 μg/ml to 50 μg/ml. Influenza virus matrix protein58–66 (IVMP58–66; GILGFVFTL) was used as an HLA-A2-specific positive control peptide. Following overnight peptide pulsing, T2 cells were harvested, washed, and stained with HLA-A2-FITC mAb for flow cytometric analyses. HLA-A2-specificity of the MP cocktail is shown as an increase in HLA-A2 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) on T2 cells. The HLA-A2 binding was dose-dependent with the MFI plateau observed at the concentration of 25 μg/ml. The values represent the mean MFI ± SE of three separate experiments.
Figure 1b. HLA-A2 stability of MP cocktail
The MP cocktail (25 μg/ml; 6.25 μg/peptide) pulsed T2 cells were washed and incubated with Brefeldin A (BFA) to block the protein transport of newly synthesized HLA-A2 molecules. The binding stability of MP was measured on T2 cells at 0, 2, 4, 6 and 14 hrs post-BFA treatment and analyzed for HLA-A2 MFI by flow cytometry. An increase in the HLA-A2 MFI was observed at each time point on T2 cells pulsed with the MP from T2 cells alone. The binding of MP was highly stable for up to 6 hours post-BFA treatment. At 14 hrs post-BFA treatment, the stability of MP cocktail was greater than the control IVMP58–66 peptide. The values represent the mean MFI ± SE of three separate experiments.
