Figure 1. C. jejuni RNase III protein features.
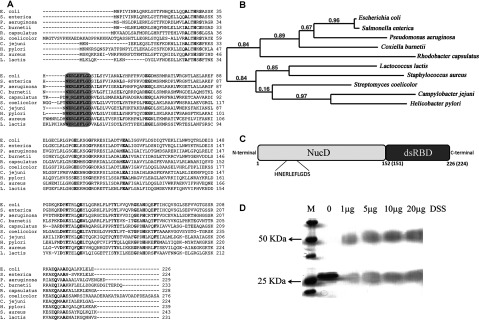
(A) Sequence alignment of RNase III from E. coli (Uniprot ID: P0A7Y0), S. enterica (Uniprot ID: E7V351), P. aeruginosa (Uniprot ID: B7UYX2), C. burnetii (Uniprot ID: P51837), R. capsulatus (Uniprot ID: Q52698), S. coelicolor (Uniprot ID: Q9ZBQ7), C. jejuni (NCBI Reference Sequence: YP_001001278), H. pylori (Uniprot ID: P56118), S. aureus (Uniprot ID: P66668) and L. lactis (Uniprot ID: Q9CHD0). Fully conserved residues are in bold, and the signature sequence of these proteins is highlighted. (B) Phylogenetic tree of RNase III from the species considered in (a). (C) Schematic representation of the domain organization of RNase III, showing the catalytic domain (NucD) (residues 1 to 151 in E. coli protein and 1 to 150 in C. jejuni protein) and the dsRNA binding domain (residues 152–226 in E. coli protein and 151–224 in C. jejuni protein). The signature sequence present in the catalytic domain is emphasized. (D) Cross-linking of RNase III from C. jejuni using DSS. Approximately 0.5 μg of protein was incubated with increasing concentrations of DSS as indicated in the figure. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining.
