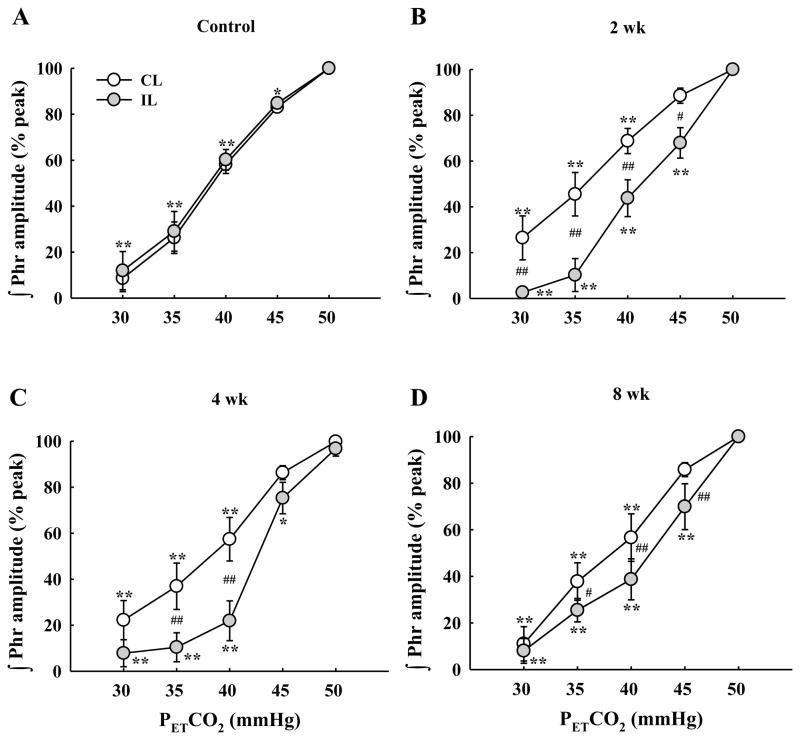
Fig. 12. Mean changes in the phrenic neurogram inspiratory burst amplitude as PETCO2 was gradually changed.
Each panel shows data from the ipsilateral (IL) and contralateral (CL) phrenic nerves in control (A), 2 wk (B), 4 wk (C) and 8 wk (D) post-C2Hx animals. All groups showed a progressive reduction in the burst amplitude of both phrenic nerves in parallel with PETCO2 reductions. Changes in bursting were indistinguishable between the two phrenic nerves in control rats (A). In contrast, the ipsilateral phrenic burst declined more severely in as PETCO2 was reduced in C2Hx animals. *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01 different from 50 mmHg data point. #: P < 0.05; ##: P < 0.01 difference between the ipsilateral and contralateral burst amplitude at the same level PETCO2.