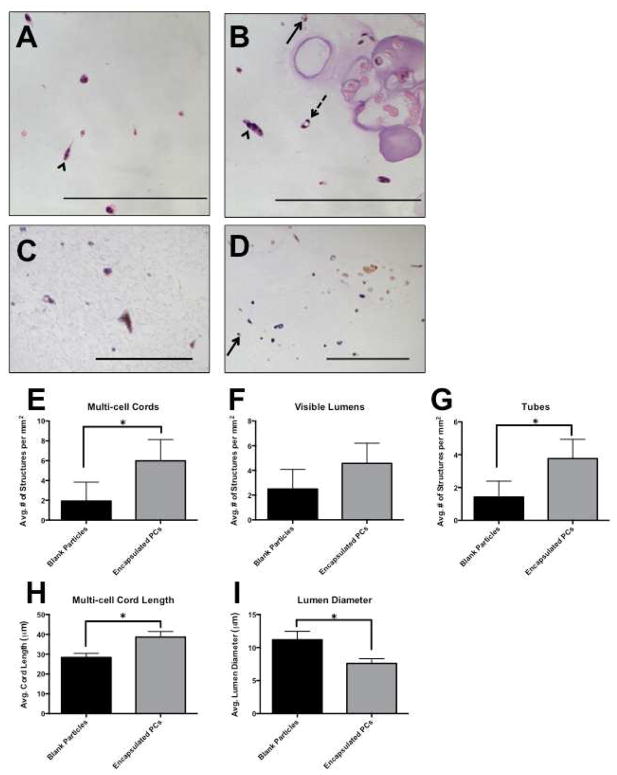
Figure 6.
Alginate-encapsulated PCs were suspended with Bcl-2-EC in protein gels to create a dual-cell, two phase 3D construct. After 7 days, gels were fixed and sectioned, and vascular structures were counted. We define cords, lumens, and tubes as separate structures: Multi-cell cords contained more than one cell, stretched out, but no lumens (arrowhead); visible lumens were all empty spaces surrounded by one or more cells (arrow, solid line), and tubes were lumens that were surrounded by two or more cells (arrow, dashed line). Encapsulated PC are outlined in grey. H&E: (A) Bcl-2-EC with blank particles. (B) Bcl-2-EC with encapsulated PC. Human CD31 staining confirmed that structures in the gel phase consisted of Bcl-2-EC only (C), and staining for SMA confirmed that PCs did not escape the particulate phase (D). Experimental groups that contained encapsulated PCs formed more multi-cell cords (E), visible lumens (F) and tubes (G). Additionally, paracrine factors released from encapsulated PCs stimulated longer multi-cell cords (H) and limited the diameter of lumens (I), when compared to gels with blank particles. Scale bars = 200 μm.