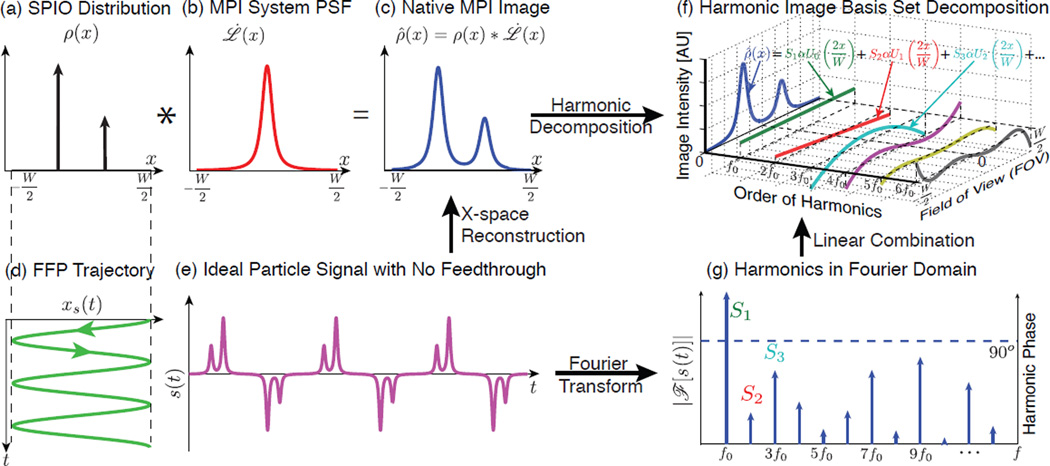
Figure 2.
Illustration of 1D MPI imaging process, x-space reconstruction and harmonic decomposition of the MPI signal in the time and image domains. (a)–(c) MPI is intrinsically LSI – the native image can be written as a convolution of the input SPIO distribution and a point spread function (PSF). (d) Basic sinusoidal scanning sequence in 1D. (e) Theoretical time domain nanoparticle signal assuming no direct feedthrough. (f) Application of the x-space reconstruction to each harmonic signal expands the native image into the MPI harmonic image basis set, which is composed of Chebyshev polynomials of the second kind. (g) The Fourier representation of the time domain signal. Note that the phase is 90° across all the harmonics from the inductive detector.