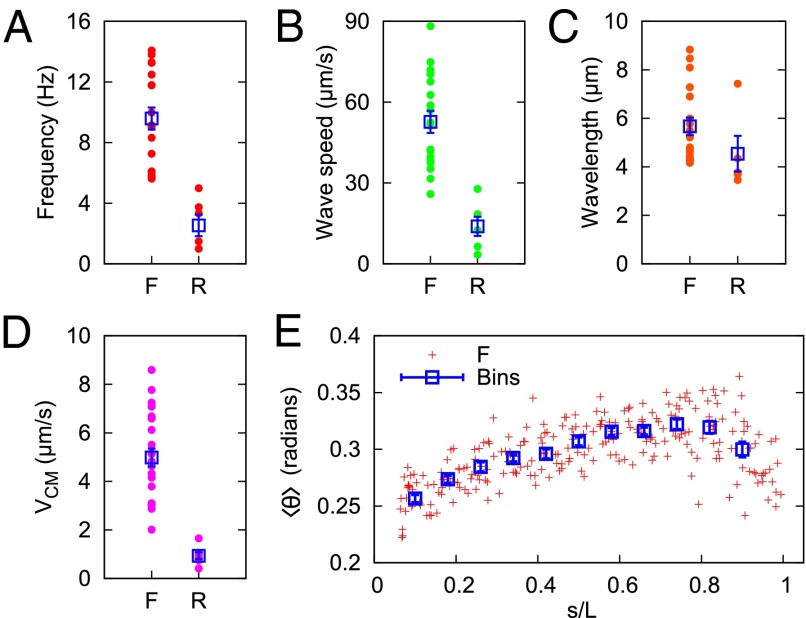
Fig. 4.
(A) Principle beat frequency component of forward (F) and reverse (R) microgamete waveforms. (B) Speed at which waves of curvature propagate along the microgamete (Materials and Methods). (C) Resulting characteristic wavelength, found by dividing wave speed by frequency. (D) Speed of the microgamete’s center of mass over a linear trajectory of around 20 μm. (E) Average curvature of forward-swimming gametes as a function of the normalized contour length (contour length s/microgamete total length L). In A–E, each point represents data from a different microgamete (from five independent infections). The boxes in A–D represent a mean value (±SEM) of forward and reverse swimming directions. The boxes in E represent data binned in increments of Δs/L = 0.08 (±SEM).