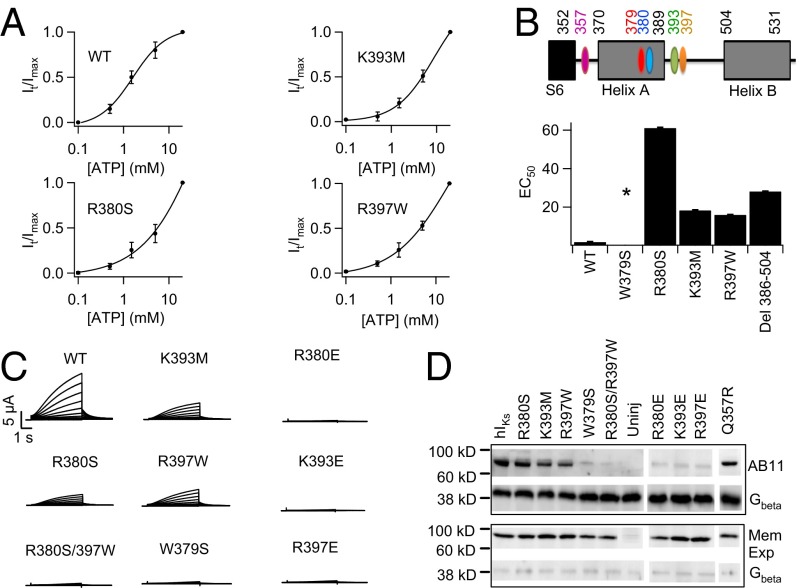
Fig. 4.
ATP binds in the C terminus of KCNQ1. (A) ATP dose–response curve of WT and key mutant IKs channels. (B) The KCNQ1 motifs important for ATP interaction (Upper) and EC50 of ATP dose–response of mutant hIKs channels (Lower). Due to insolubility of ATP above 20 mM, dose–response for some mutants did not reach saturation, leading to underestimated EC50. Asterisk indicates no current expression. (C) Whole-cell currents of mutant hIKs. (D) Western blot to detect AB11 labeling of mutant IKs. (Upper) AB11 labeling of mutant IKs and Gβ in the whole-cell lysate to indicate similar inputs. (Lower) Western blot probing for biotinylated mutant IKs and Gβ in the membrane. Gβ is a cytoplasmic protein.