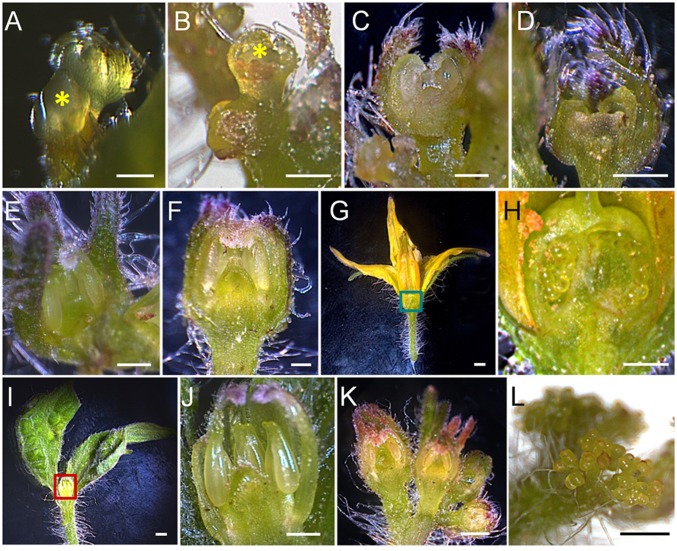
Fig. 2.
Microscopic observation of PPT phytoplasma infection-induced changes in meristem fate and flower morphology. (A and B) Stage 3 floral buds (0.5 mm, indicated by yellow asters) of mock-inoculated (A) and phytoplasma-infected (B) plants. (C and D) Stage 6 (1 mm) floral buds of mock-inoculated (C) and phytoplasma-infected (D) plants. (E and F) Stage 8 (2 mm) floral buds of mock-inoculated (E) and phytoplasma-infected (F) plants. (G) Longitudinal section of a mature flower from a mock-inoculated plant. (H) A close-up view of the green-boxed part of G, showing carpel with ovules. (I) Longitudinal section of a BB from a phytoplasma-infected plant. (J) A close-up view of the red-boxed area of I, showing aborted three inner whorl organs. (K) Normal floral transition leading to formation of typical tomato inflorescence and flowers. (L) A phytoplasma infection-induced CLI composed of dividing sympodial IMs. (Scale bar: 0.5 mm.)