Figure 5. Quantification of the CTD effect in S2 cell culture.
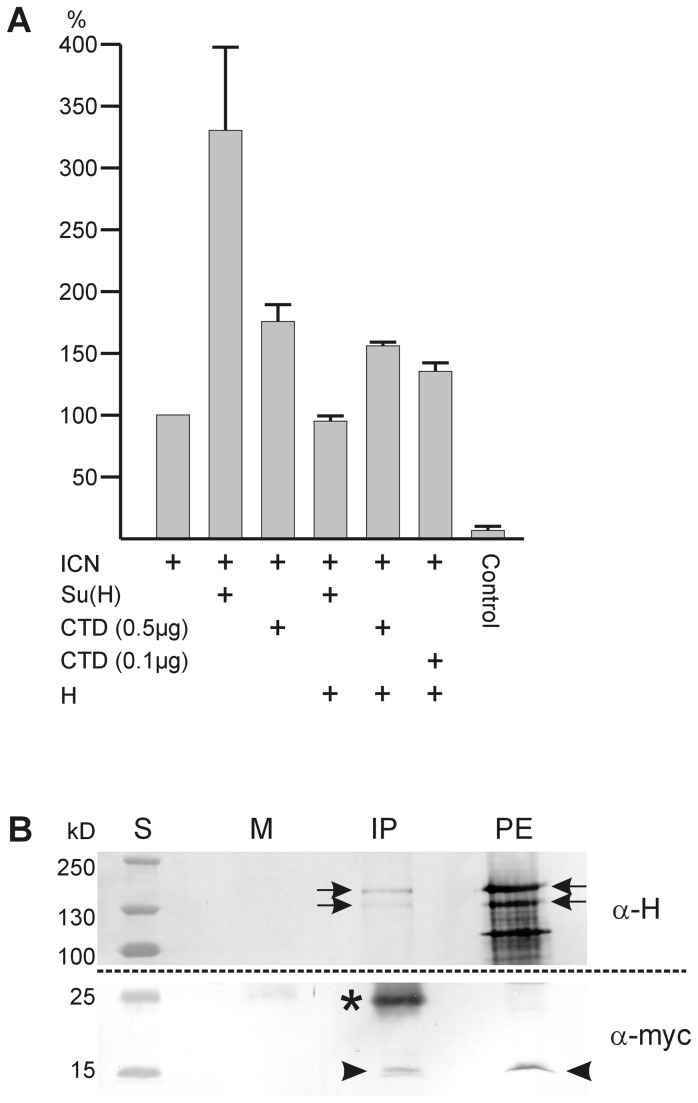
A) Transfection of S2 cells with a luciferase reporter gene containing several Su(H) binding sites was performed and activity measured in the presence of the given constructs. The activation by ICN was taken as 100%; this is enhanced about 3.5 fold by addition of Su(H). Addition of myc-CTD activates as well, although to a lesser degree, despite its lack of DNA-binding. The activation by exogenous Su(H) is effectively repressed by exogenous full length Hairless (H). Interestingly, Hairless is less able to suppress activation by myc-CTD. Control is empty pMT-vector. Three independent experiments were sampled, standard deviation is indicated.
B) Co-immunoprecipitation was performed on protein extracts from fly heads overexpressing myc-CTD and Hairless in the developing eye (genotype: gmr-Gal4 / +; UAS-HFL UAS-myc-CTD/ +). Anti-myc antibodies were used for precipitation (IP), detection was with anti-Hairless A (α-H; upper blot 7.5% PAGE) and anti-myc antisera (α-myc; lower blot 12% PAGE), respectively. PE, protein extract as input control; M, mock control; S, protein ladder (sizes in kilodaltons, kD). Myc-CTD has an expected size of 13.8 kDa (arrowheads), the two Hairless isoforms are of approximately 150 and 120 kDa (arrows). The smaller bands in the protein extract detected by anti-H antibodies are most likely degradation products; * light chain immunoglobulins.