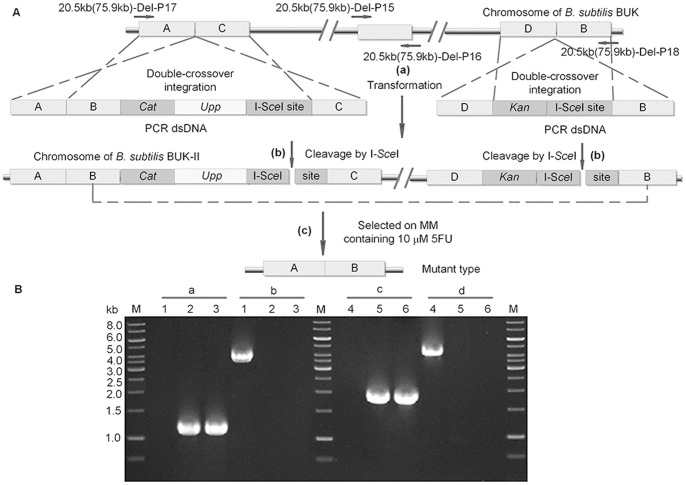
Figure 5. Markerless deletion of large chromosomal regions stimulated by DSB.
A. (a) Two dsDNA fragments were generated by fusion PCR and integrated into genome by double-crossover events. (b) The endonuclease I-SceI was expressed from pEBS-cop1 under the induction of xylose, and the genome of B. subtlis BUK-II was subjected to I-SceI cleavage. (c) Deletion mutants were isolated on MM plate containing 10 µM 5FU and confirmed by PCR. A, B, C, D represent DNA segments selected for homologous recombination. B. Verification of the 20.5 kb and 75.9 kb deletions in BUK by PCR. Fragments were amplified using the primer pairs 20.5 kb-DEL-P15/20.5 kb-DEL-P16 (a), 20.5 kb-DEL-P17/20.5 kb-DEL-P18 (b), 75.9 kb-DEL-P15/75.9 kb-DEL-P16 (c), 75.9 kb-DEL-P17/75.9 kb-DEL-P18 (d). 1 kb DNA Ladder (Fermentas) was used as a molecular weight marker (lane M). (a) Amplification of the ydcR gene (534334–535389 SubtiList coordinates) in the 20.5 kb DNA region of B. subtilis; (b) Amplification of the 20.5 kb DNA fragment of B. subtilis; (c–d) Confirmation of the 75.9 kb deletion of BUK was the same as that of 20.5 kb deletion. Amplification of the pksG gene (1789763–1791405 SubtiList coordinates) in the 75.9 kb DNA region of B. subtilis (c) and amplification of the 75.9 kb DNA fragment of B. subtilis (d). Each lane showed amplified DNA generated from a DNA template: lane 1, BUKΔ20.5 kb; lane 2, BUK-II (20.5); lane 3, BUK; lane 4, BUKΔ75.9 kb; lane 5, BUK-II (76.9); lane 6, BUK.