Figure 1. In vitro studies of ICG loaded monocytes.
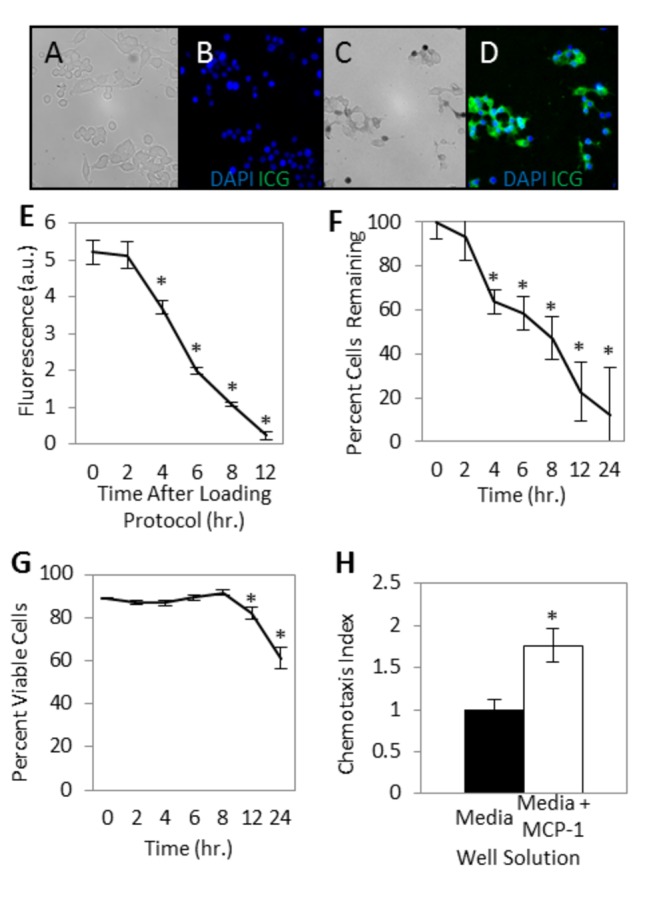
(A, B) Representative images, RAW 264.7 mouse monocytes incubated in media alone and stained with DAPI. (A) Brightfield image. (B) DAPI blue nuclear staining and no NIR fluorescence (pseudocolor green). (C, D) Representative images, Monocytes after incubation in media with ICG solution and stained with DAPI. (C) Brightfield image. (D) DAPI fluorescence (blue) and NIR ICG fluorescence (pseudocolor green). (E) Ex vivo cellular fluorescence over time. Monocytes incubated in media with ICG display an average NIR fluorescence of 5.22±0.34 arbitrary units (a.u.) above background (control non-ICG loaded cells) following the loading procedure, decreasing toward background over the following 12 hours (N=10). (F, G) Yield and viability of monocytes after ICG loading procedure. (F) Cell yield, after maintaining the cells ex vivo in culture media and washing and centrifuging at each time point, decreases over the first 24 hours after loading with ICG. (G) Viability of cells remains greater than 80% for more than 12 hours (N=10). (H) ICG loaded monocyte chemotactic capacity. Chemotactic index is the number of cells migrating through the chemotaxis filter toward media with the chemoattractant MCP-1 relative to the number of cells migrating through the chemotaxis filter toward media alone. The average number of migrated ICG-loaded monocytes per five high powered fields was 86.0±27.8 with MCP-1 in the bottom well, and 48.9±16.5 with chemotaxis media alone in the bottom well (N=3). All error bars represent SEM. *P<0.05.
