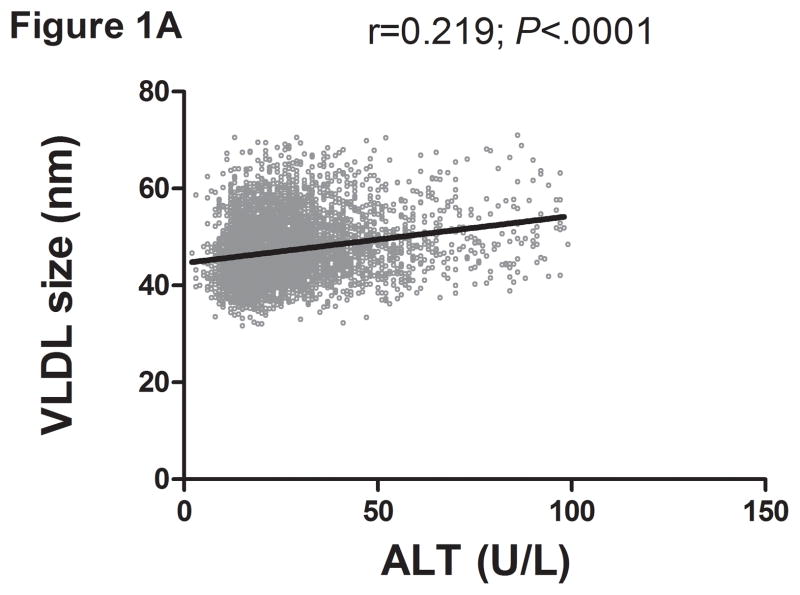
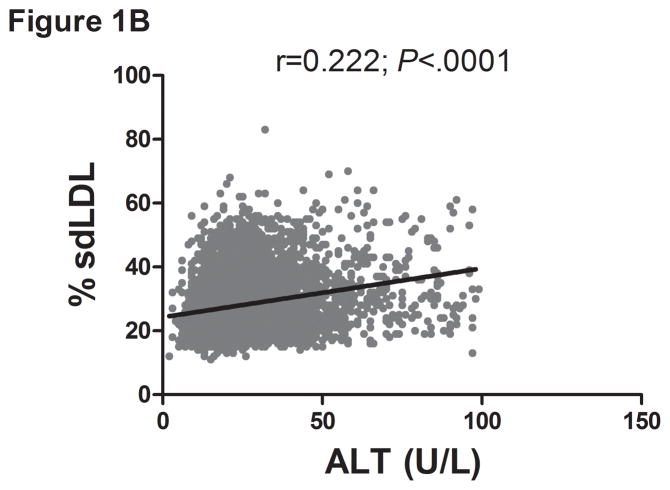
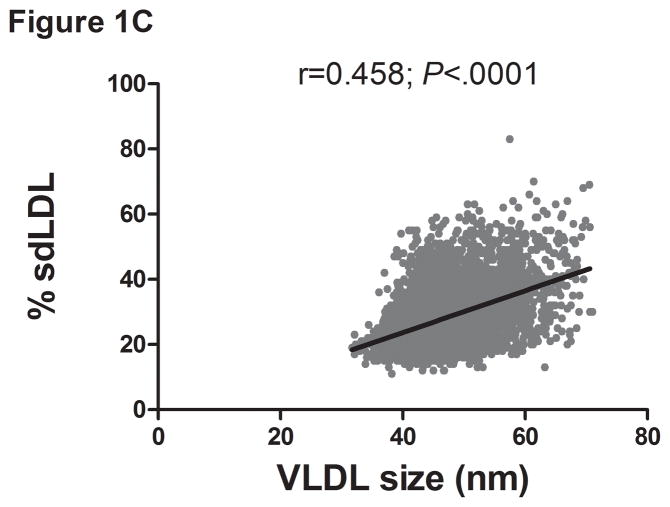
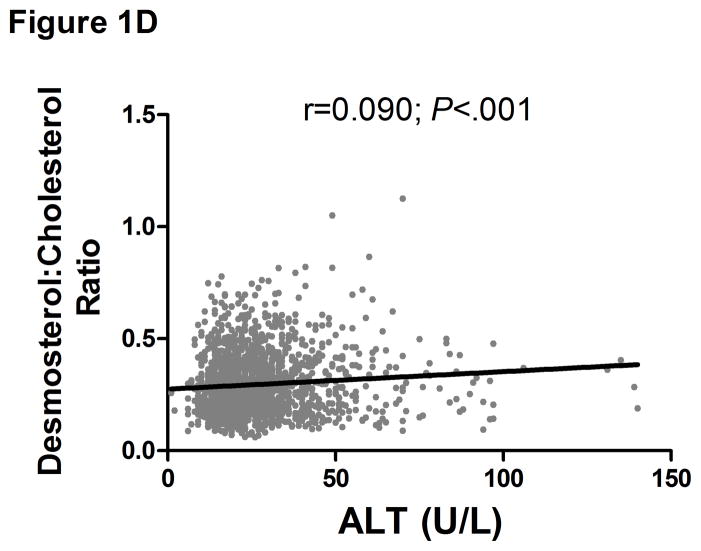
Figure 1.
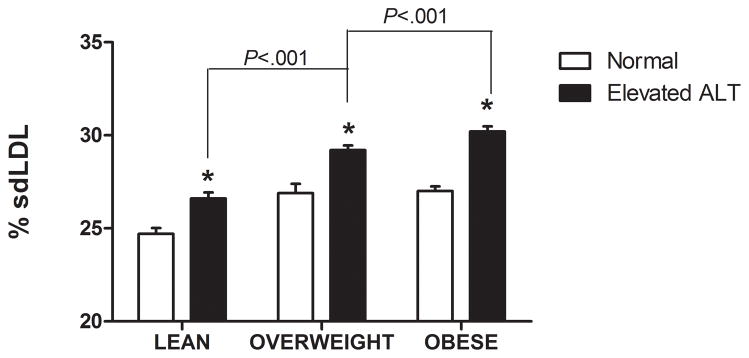
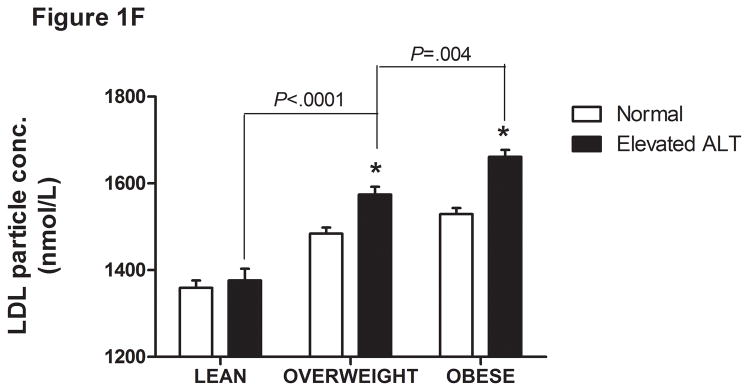
Serum ALT levels are directly related to very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) size (Figure 1A), % small dense LDL cholesterol (sdLDL-C) (Figure 1B), and desmosterol:cholesterol ratio (Figure 1D) in an apparently healthy population. Percent sdLDL-C is directly related to VLDL size (Figure 1C). Percent sdLDL-C and LDL-particle concentrations (LDL-P) increase from lean to overweight to obese cohorts (P <.001) (Figure 1D & 1E). Although % sdLDL-C and LDL-P were similar between overweight and obese individuals with normal ALT, they increased dramatically in those with elevated ALT (P <.01). (*P <.05 between normal and elevated ALT). All data represented as means ± S.E.M. Elevated ALT is defined as > 19 U/L in women and >31 U/L in women.