Figure 3.
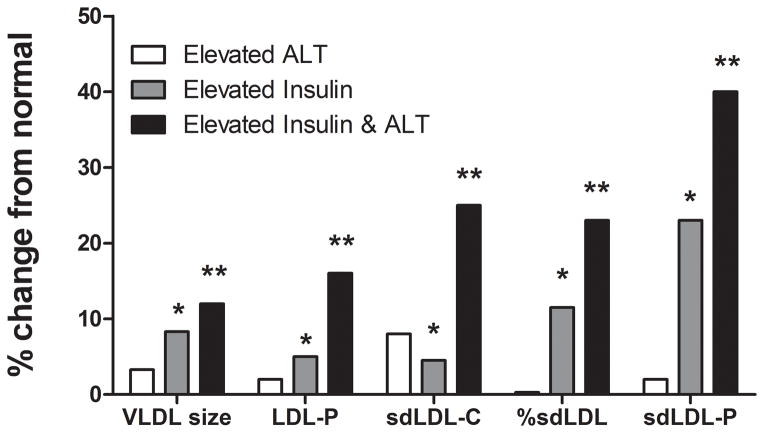
Presence of elevated ALT was associated with worsening expanded cardiovascular profile in both individuals with normal or elevated serum insulin concentrations. There was a synergistic increase seen in serum LDL particle concentrations (LDL-P), small dense LDL cholesterol (sdLDL-C), % small dense LDL-C, and small dense LDL-particle concentrations (sdLDL-P) in individuals with both elevated insulin and elevated ALT concentrations. The increase in VLDL size was additive in individuals with elevated ALT and insulin concentrations. (*P <.001 elevated ALT vs elevated insulin; ** P <.001 elevated insulin vs. elevated insulin and elevated ALT). Elevated ALT is defined as > 19 U/L in women and >31 U/L in women.