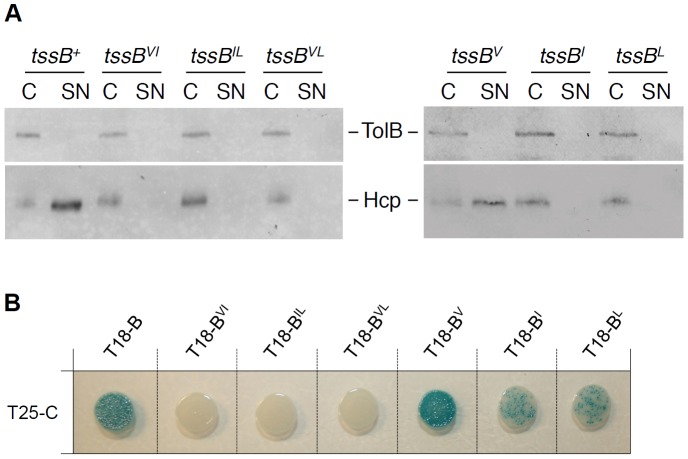
Figure 4. Mutagenesis study of the hydrophobic motif of the TssB1 α-helix.
(A) Hcp release assay. HcpFLAG release was assessed by separating whole cells (C) and culture supernatant (SN) fractions from 2×109 ΔtssB1 cells producing TssB1 (tssB+) or TssB1 bearing double or single substitutions within the hydrophobic motif (tssBVI, V106W-I110W; tssBIL, I110W-L117W; tssBVL, V106W-L117W; tssBV, V106W; tssBI, I110W; tssBL, L117W). Proteins were separated by 12.5%-acrylamide SDS-PAGE and Hcp and TolB were immunodetected using anti-FLAG monoclonal (lower panel) and anti-TolB polyclonal (upper panel) antibodies. (B) Bacterial two-hybrid assay. BTH101 reporter cells producing the T25 domain of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase fused to TssC1 (T25-C) and the T18 domain fused to TssB1 (T18-B) or TssB1 variants bearing substitutions within the hydrophobic motif (T18-BVI, V106W-I110W; T18-BIL, I110W-L117W; T18-BVL, V106W-L117W; T18-BV, V106W; T18-BI, I110W; T18-BL, L117W) were spotted on X-Gal indicator LB agar plates.