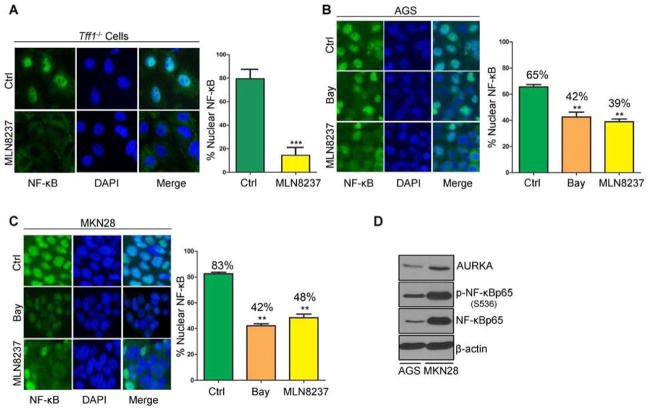
Figure 2. AURKA regulates NF-κBp65 nuclear translocation ex vivo and in vitro.
A) Antrum epithelial cells were extracted from Tff1-knockout mice. Selectively cultured epithelial cells were treated with vehicle (ctrl) or MLN8237 (500 nmol/L) and subjected to immunofluorescence analysis of NF-κBp65. Original magnification is shown at ×100. Treatment with MLN8237 significantly reduced nuclear NF-κBp65–positive staining relative to vehicle-treated control (p<0.001). B–C) NF-κBp65 immunofluorescence in AGS (B) and MKN28 (C) cells after 30 min treatment with NF-κB inhibitor Bay 11-7085 (10 μmol/L) or AURKA inhibitor MLN8237 (500 nmol/L). Nuclear localization of NF-κBp65 is shown in green. DAPI (blue) was used as a nuclear counterstain. Graphs indicate the quantification of nuclear NF-κBp65–positive staining in at least 200 counted cells presented as a percentage. D) Western blot analysis of AURKA, p-NF-κBp65 (S536), and NF-κBp65 proteins in AGS and MKN28 cell lines suggesting a correlation between AURKA and p-NF-κBp65 (S536) protein levels.