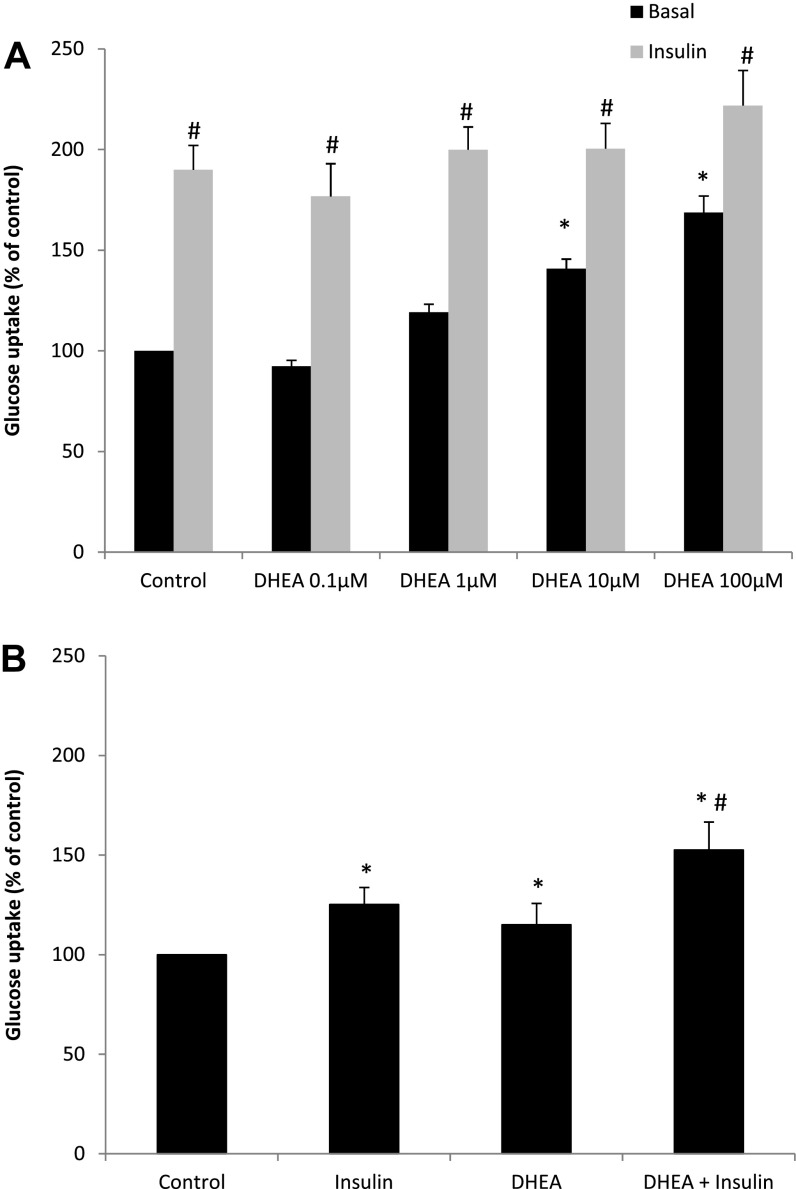
Fig. 7.
DHEA increases basal but not insulin-dependent glucose uptake in adipocytes. A: in mature Chub-S7 adipocytes, DHEA (≥1 μM) significantly increased basal glucose uptake (black bars) but not insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (20 nM; gray bars). B: in human primary adipocytes, insulin increased glucose uptake to 125 ± 8.6% (P < 0.05) and 25 μM DHEA to 115 ± 10.7% (P < 0.05) compared with basal. Addition of insulin to DHEA increased glucose uptake to 133 ± 14.0% compared with DHEA alone (P < 0.05). Data are presented as %control from 5 experiments performed in triplicate [Chub-S7 control DPM = 5,257 (A); human primary adipocytes control DPM = 5,212 (B)]. *P < 0.05 vs. control; #P < 0.05 vs. DHEA treatment.