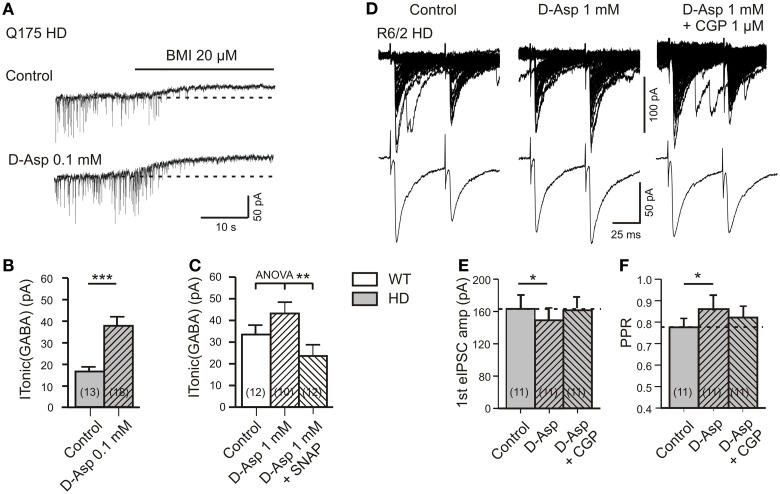
Figure 5.
Effects of D-aspartate on ITonic(GABA) and GABA(B) receptor-mediated presynaptic depression of synaptic GABA release. (A–C) Experiment with Q175 WT and HD. Recordings in the presence of DNQX (10 μM), APV (50 μM), and LY341494 (40 μM). (A) Sample traces from a Q175 HD SON in the absence and presence of D-aspartate (0.1 mM). Note the larger ITonic(GABA) after 10 min treatment of HD slices with D-aspartate. (B) Quantification of the results from Q175 HD mice. Significance level according to Mann–Whitney test. (C) ITonic(GABA) of WT SONs treated with 1 mM D-aspartate for 5 min. Note the highly significant decrease in the presence of SNAP5115 (40 μM). Significance level according to One-Way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni correction [F(2, 31) = 6.603, p = 0.0041]. The data sets represented in the three columns are independent, not matched. (D–F) eIPSCs in R6/2 WT and HD SONs in the presence of APV (50 μM), DNQX (20 μM), and LY341494 (40 μM). (D) Records of averaged eIPSCs from one and the same HD SON under the indicated conditions. Note the rescue of tonic GABA(B)-mediated depression of synaptic GABA release in HD after treatment of 1 mM D-aspartate for 5 min. (E,F) Quantification of the results from HD SONs tested for changes in eIPSC amplitude (E) and PPR (F) in the presence of D-aspartate and D-aspartate plus CGP. The indicated differences between Control and D-aspartate reflect the amount of tonic presynaptic depression of synaptic GABA release according to Wilcoxon's matched-pairs signed rank test after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparison. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.