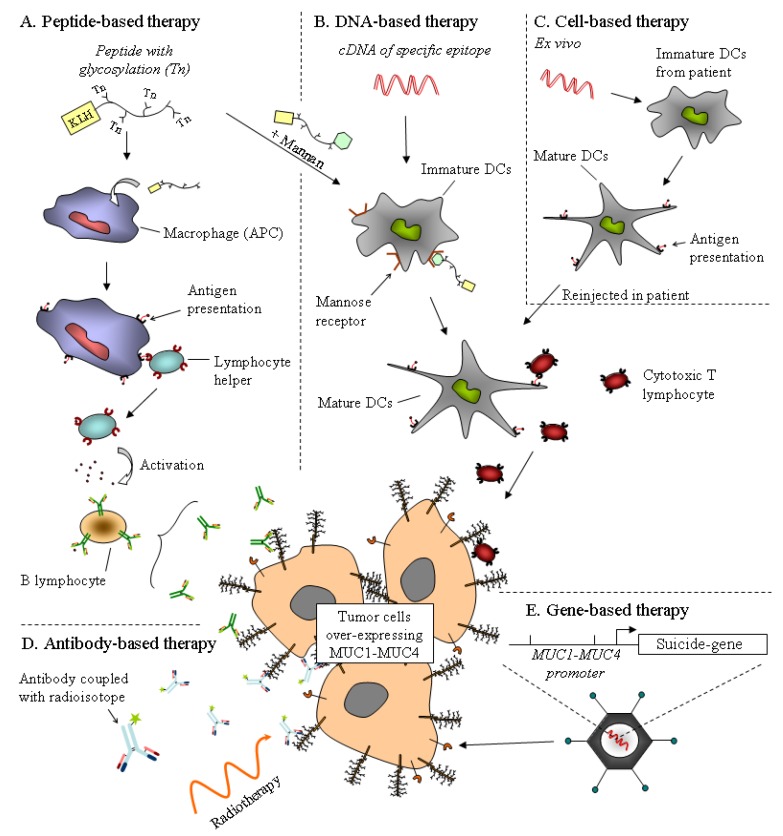
Figure 2.
Strategies for mucin-based therapies already used in phase trial. The aim of antigen-based therapy, by the use of a peptide or a cDNA derived from mucin epitopes, is to activate the immune system against tumor cells overexpressing the mucin. (A) The glycosylated mucin peptide, with KLH adjuvant, activates the humoral response by the activation of antigen-presenting cells (APC). The efficiency of this peptide may be increased with a mannan epitope recognized by a mannose receptor on dendritic cells (DCs), which in turn activates the cytotoxic response. (B) DNA vaccine encoding a specific mucin epitope is incorporated by DCs and activates the cytotoxic T lymphocyte. (C) Cell-based therapy is an alternative of DNA vaccine. Immature DCs extracted from the patient are incubated with DNA encoding the mucin epitope. Activated DCs exhibiting mucin antigen are injected into the patient. (D) Antibody-based therapy. Use of antibodies is promising for the detection and treatment of cancer. Antibodies against mucin epitopes are coupled with a radioisotope for radiotherapy ((131)I-PAM4) or a cytotoxic drug to target tumors. (E) Gene-based therapy. Promoter of mucin may be used to deliver a cytotoxic agent on tumor cells.