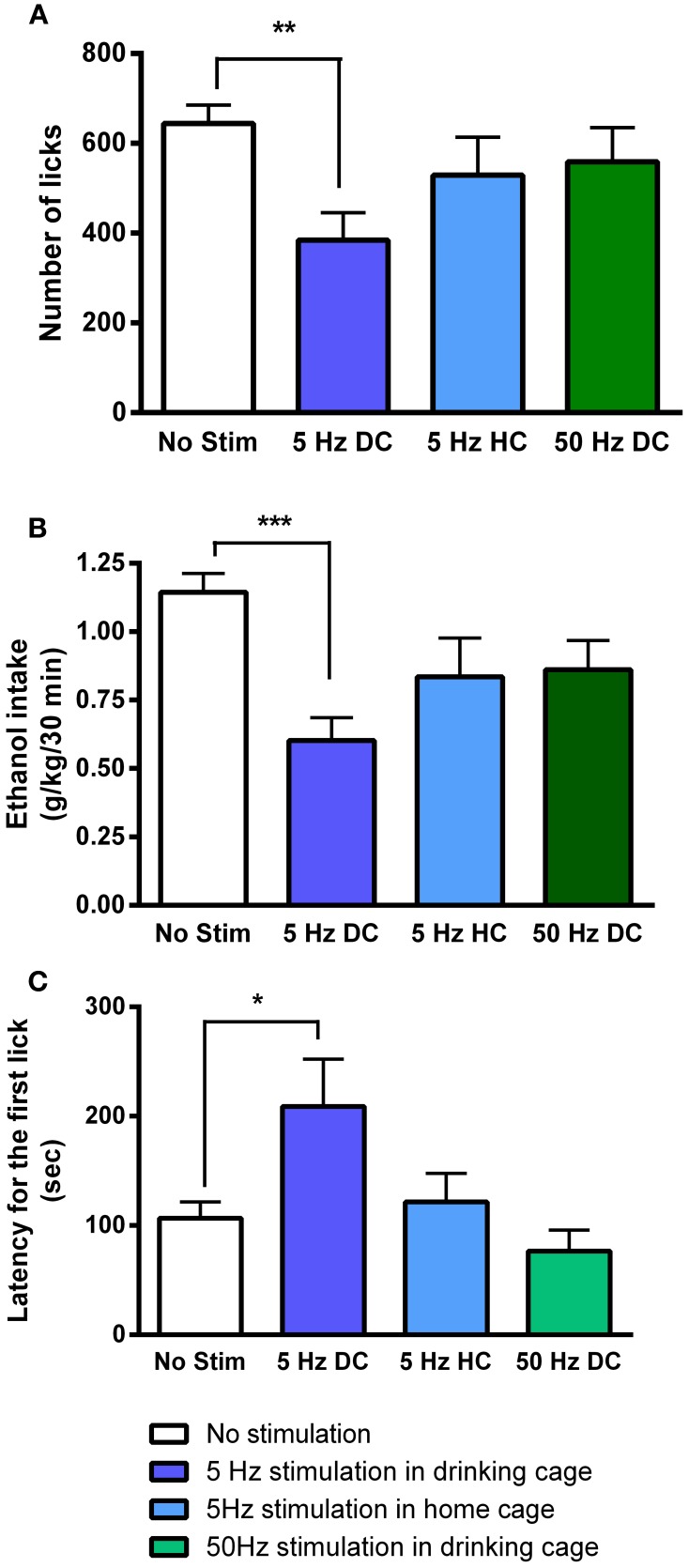
Figure 6.
Tonic dopamine release alters ethanol drinking measures only when optogenetic stimulation is applied in the drinking cage. Bar graphs illustrate averaged values of (A) number of licks, (B) total dose of ethanol consumed (g/kg), and (C) latency for the first lick (s) across multiple sessions. The sessions were performed in the drinking cage (DC) with no stimulation (No Stim), with 5-Hz (5 Hz DC) and with 50-Hz stimulation (50 Hz DC), applied in the first 10 min, and in the home cage (HC, 10 min immediately prior to being placed in the drinking cage) with 5-Hz stimulation (5 Hz HC). The effect of 5-Hz stimulation applied in the drinking cage compared to No Stim was significant for all drinking parameters. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the session when no stimulation was applied.