Figure 1.
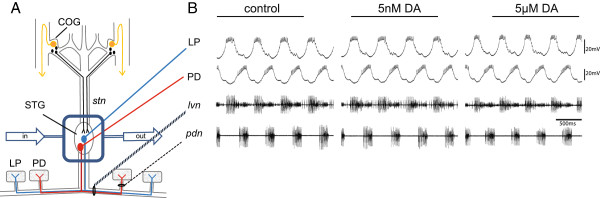
Stomatogastric nervous system and experimental method. A. The stomatogastric nervous system (STNS) was dissected from the animal and pinned in a Sylgard dish. A petroleum jelly well was constructed around the stomatogastric ganglion (STG). There are ~30 neurons in the STG; two are drawn. Saline, with or without drugs, was superfused into the well surrounding the STG. Neurons in the commissural ganglia (COG) and esophageal ganglion provide descending modulation that remained intact until voltage-clamp. LP was identified using a combination of intra and extracellular recordings. B. Pyloric neurons spontaneously produce a triphasic rhythmic output (Control-Left Traces). The top two traces represent intracellular recordings from the lateral pyloric (LP) and pyloric dilator (PD) cells, while the bottom traces represent extracellular recordings taken from the lateral ventricular nerve (lvn) and pyloric dilator nerve (pdn). The application of 5nM DA produces no change in the LP rhythmic output (Middle Traces). Application of 5 μM DA (Right Traces), however, alters LP activity [14]. In 5 μM DA cycle frequency is increased and LP burst duration is a decreased [24].
