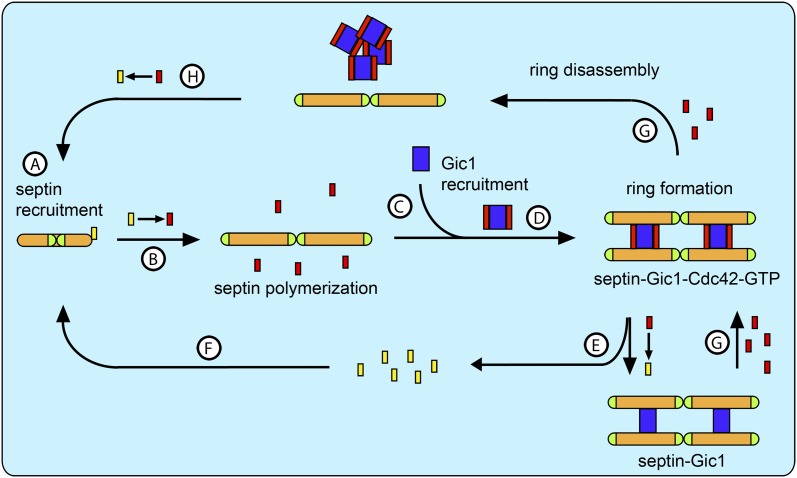
Figure 16. Model for septin recruitment, ring formation and disassembly.
(A) Cdc42-GDP recruits septin complexes to the bud site. (B) At the bud site Cdc24 catalyzes the nucleotide exchange of Cdc42, which recruits its effector Gic1. (C) Septins polymerize. (D) Gic1 scaffolds and stabilizes septin filaments and forms septin-Gic1-Cdc42-GTP filament cables that are used for building the septin ring. (E) Cdc42-GTP is not necessary for the stability of the filament cables and upon GTP hydrolysis dissociates from the septin-Gic1 complexes. (F) Cdc42-GDP recruits more septin complexes to the bud site. (G) During cell division the local concentration of Cdc42-GTP increases by the up-regulation of Cdc24. This leads to a dissociation of the septin-Gic1-Cdc42-GTP filament cables and the septin ring disassembles. (H) After Cdc42-GAP catalyzed hydrolysis, Cdc42-GDP binds to the septin filaments and disassembles them to octamers. Septins are depicted as orange rods. Green caps indicate Cdc11. Gic1 is depicted as a blue rectangle. Cdc42-GTP and Cdc42-GDP are depicted as red and yellow rectangles, respectively.