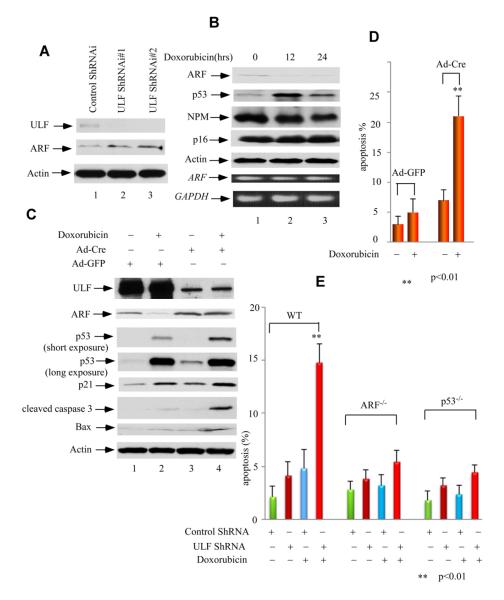
Figure 5. Loss of ULF stabilizes ARF and promotes p53-dependent apoptosis mediated by DNA damage in MEFs.
(A) Western blot analysis of cell extracts with an anti-ARF, ULF, and actin antibodies from ULF-knockdown primary MEFs by ShRNA (lanes 2-3) versus control primary MEFs (lane 1).
(B) Western blot analysis of cell extracts from primary MEFs harvested at indicated time points after 0.2 mg/ml doxorubicin treatment by anti-ARF, p53, NPM and p16 antibodies. ARF and GAPDH mRNA expression levels by RT-PCR were shown at lower panels.
(C) Western blot analysis of cell extracts with anti-ULF, ARF, p53, p21, cleaved caspase 3, Bax and PUMA antibodies from ULF-deleted primary MEFfl/fl cells by Ad-CMV-Cre (lanes 3, 4) versus Ad-CMV-GFP infected primary MEFfl/fl cells (lanes 1, 2), and followed by doxorubicin treatment (lanes 2, 4) or without treatment (lanes 1, 3).
(D) Apoptotic cells (Sub-G1) according to DNA contents (PI staining) were counted for the same cells in Figure 5C. Error bars represent s.d. (n=3).
(E) ULF depletion sensitizing DNA damage-mediated apoptosis in primary MEF cells is ARF- and p53-dependent. Apoptotic cells (Sub-G1) according to DNA contents (PI staining) were counted for primary wild type, p53−/− and ARF −/− MEFs infected with ULF ShRNA versus control ShRNA lenti-virus, subsequent puromycin selection and followed by 0.2 mg/ml doxorubicin treatment by FACS. Error bars represent s.d. (n=3). See also Figure S5.