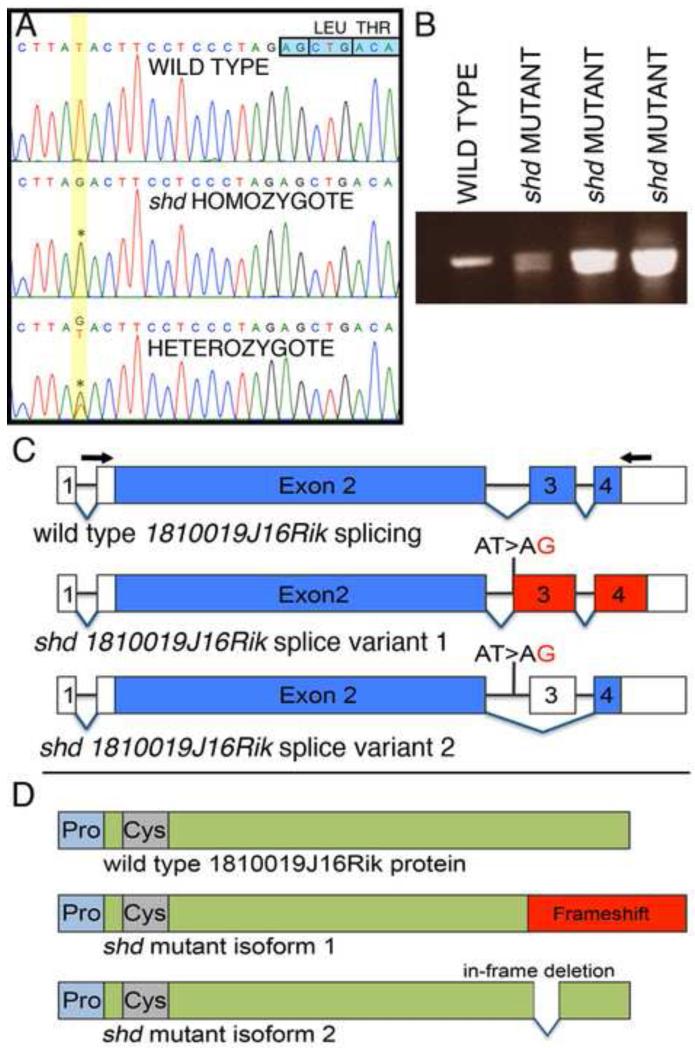
Figure 5. Identification of a point mutation within the 1810019j16Rik locus, causing splicing defects in shd mutants.
(A) Sequence traces from wild type, heterozygous and homozygous shd embryos. In shd mutants and carriers, there is a T>G transversion (asterisks) 14 bases upstream of the start of exon 3 (indicated by the boxed nucleotides, top right) of the Kdf1 (1810019J16Rik) transcript. (B) RT-PCR across exons 2-4 of the Kdf1 transcript showing a single band in wild type and two bands in shd homozygotes. (C) Representation of the splice variants in wild type and shd mutant. The Kdf1 mRNA spans four exons (exon 2-4 are coding exons). The shd mutation, a T>G transversion in intron 2, results in either a frame shift (splice variant 1) or skipping of exon 3 altogether (splice variant 2). Blue: coding exons; red: frame shift regions; white: untranslated regions. Arrows indicate the position of primers used for RT-PCR in (B). (D) Schematic representation of the Kdf1 protein. The predicted protein of Kdf1 does not contain conserved protein domains, except slightly proline-rich (light blue) and cysteine-rich (grey) regions in the N-terminus of the protein. The frame shift in the shd mutant isoform1 will result in a longer protein with the C-terminal being out of frame (red). Alternatively, skipping of exon 3 will give rise to a truncated protein with a 24 amino acid in-frame deletion.