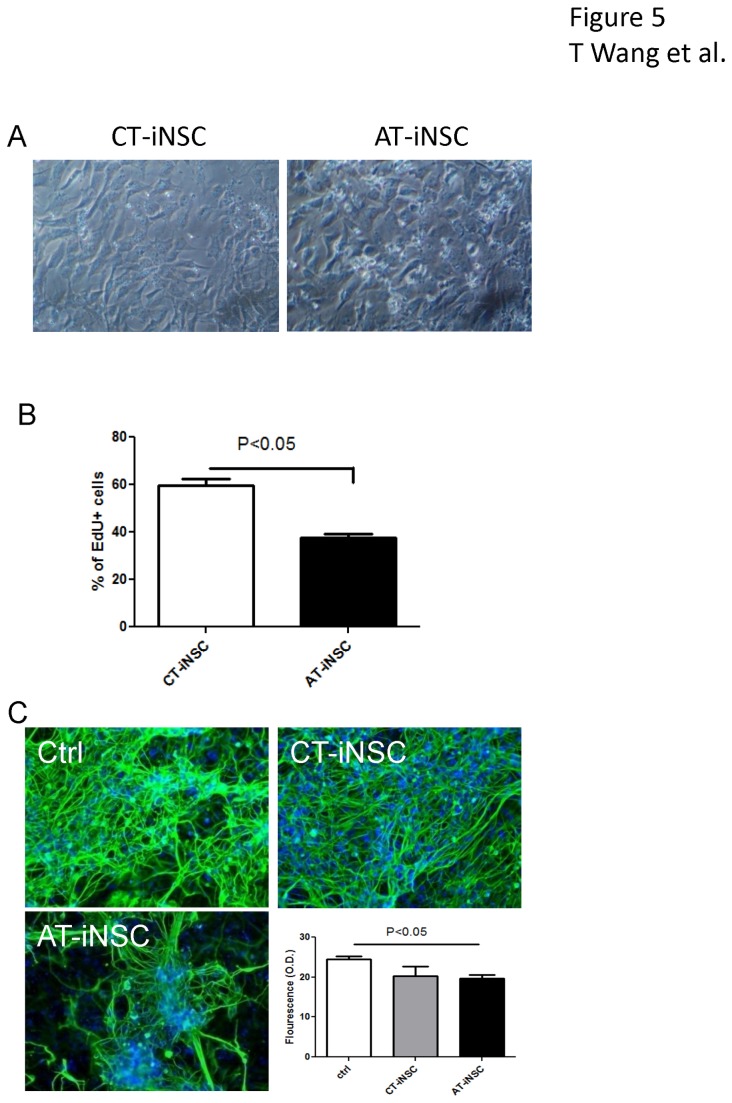
Figure 5. Inhibition of neurogenesis by activated autologous T cells on induced neural stem cells.
Induced neural stem cells derived from adult peripheral CD34+ cells were cocultured with restive (CT) or activated autologous T cells (AT) for 24 hours. (A) After washing with PBS three times, no adherent T cells were observed in induced neural stem cells co-cultivated with restive T cells (CT-iNSC), while adherent T cells were observed in cultures of induced neural stem cells with activated T cells (AT-iNSC). (B) EdU incorporation assay was used to determine the proliferation of iNSC after 24 hours of co-culture. (C) After 7 days in neuronal differentiation medium, neuronal differentiation was studied by immunostaining for βIII-tubulin. The fluorescence was detected using a plate reader at excitation wavelength 495 nm and emission wavelength 519 nm. AT-iNSC coculture resulted in significantly decreased neuronal differentiation compared to non co-cultured control. Morphologically, AT treatment resulted in fewer neurons, which were more locally aggregated, compared to CT treated groups.