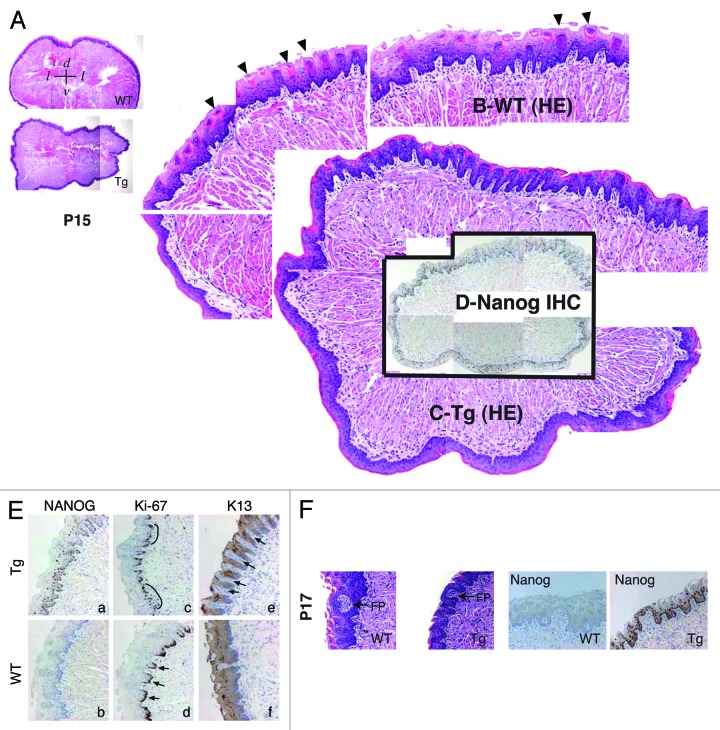
Figure 3. Abnormal differentiation in the K14-NanogP8 Tg tongue epithelia. (A–D) Gross images of the P15 WT and L1 Tg tongue. A. Representative composite images of a P15 WT (top) and a P15 L1 Tg (bottom) tongue sections stained for H and E. The orientations of the sections were indicated: d, dorsal; v, ventral; l, lateral. (B and C) Enlarged composites showing the presence of differentiated filiform papillae in the WT tongue (B; arrowheads), which were lacking in the Tg tongue (C). (D) NanogP8 staining in the Tg tongue (original magnification, ×40). The WT tongue did not show NanogP8 staining (not shown). (E) Representative IHC images of P15 WT and L1 Tg tongue epithelium stained for Nanog, Ki-67, and K13. Arrows indicate increased numbers of K13-negative dermal papillae in the Tg tongue. Note that in WT epithelium the Ki-67 cells localized mainly to the base of retelike prominences (D, arrows) but in Tg epithelium the Ki-67 cells were often contiguous (C, black lines). (F) Representative H and E and Nanog IHC images from a pair of P17 WT and L1 Tg tongue epithelium. FP, fungiform papillae. Original magnifications, ×200.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.