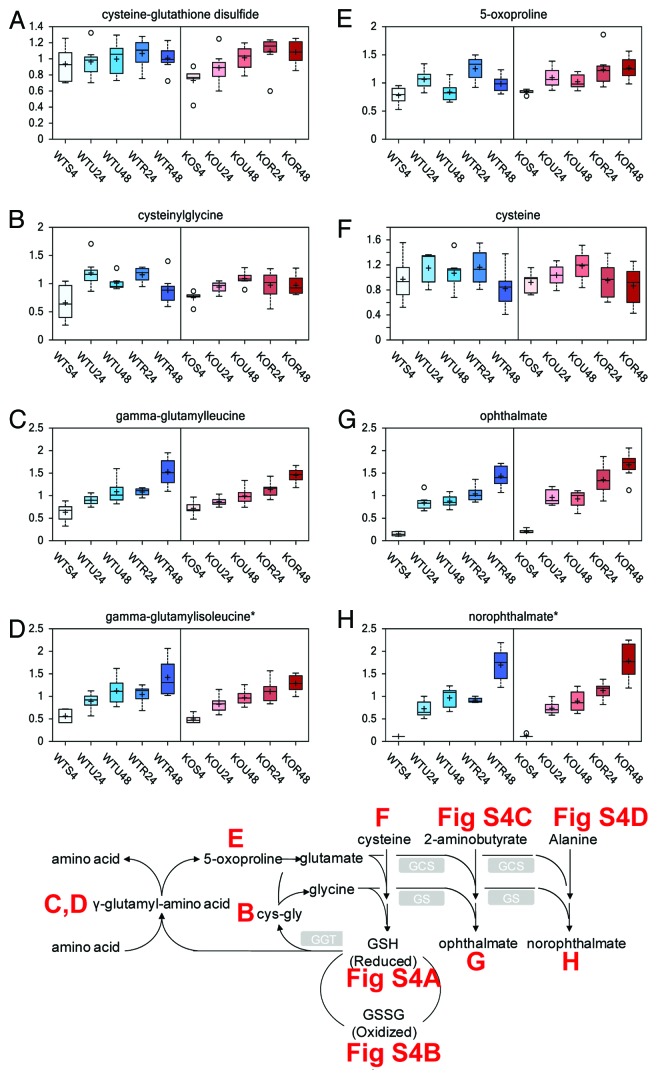
Figure 4. Glutathione pathway. Glutathione can be found in the cell in oxidized (glutathione disulphide, GSSC) and reduced (glutathione, GSH) form. Reduced glutathione can be either directly formed from glutathione disulfide as the result of activity of glutathione reductase or from conjugation of L-cysteinyl-glycine with (L)-glutamic acid catalyzed by gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT). L-Cysteinyl-glycine is formed as a result of glutathione conjugation to the L-amino acid moiety catalyzed by GGT. This reaction results in formation of gamma-(L)-glutamyl-aminoacid which is converted by gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase to the 5-oxo-(L)-proline and L-amino acid. 5-Oxo-(L)-proline is then reduced to (L)-glutamic acid. Glutathione synthetase (GCS and GS) catalyzes subsequent conjugation of gamma-(L)-glutamyl-(L)-cysteine and glycine to form glutathione. The effect of rapamycin exposure for 24 or 48 h is shown on cysteine-glutathione disulphide (A), cysteinylglycine (B), gamma-glutamylleucine (C), gamma-glutamylisoleucine (D), 5-oxoproline (E), cysteine (F), ophthalmate (G), norophthalmate (H). See Figure 1 for color and legend code.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.