Table 5.
Simulation results on the variable selection frequency 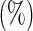
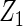 |
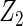 |
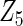 |
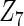 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Ave. (0.4) | Hetero. (0, 0) | Ave. (0.43) | Hetero. (0.17, −0.13) | Ave. (−0.23) | Hetero. (0.23, −0.06) | Ave. (−0.23) | Hetero. (−0.47, 0.23) |
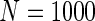 | ||||||||
| Cohort interaction | 99.0 | 8.5 | 98.5 | 19.0 | 67.0 | 36.5 | 65.0 | 87.0 |
| CAP | 100 | 2.0 | 99.0 | 19.0 | 82.0 | 42.5 | 88.0 | 86.5 |
| cagLASSO | 99.0 | 1.5 | 98.5 | 10.5 | 77.5 | 33.0 | 92.0 | 84.5 |
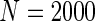 | ||||||||
| Cohort interaction | 100 | 5.0 | 100 | 35.0 | 95.5 | 58.0 | 95.5 | 100 |
| CAP | 100 | 5.5 | 100 | 32.5 | 98.5 | 75.5 | 100 | 100 |
| cagLASSO | 100 | 0.0 | 100 | 19.0 | 96.0 | 54.5 | 100 | 99.5 |
| Different cohort sizes | ||||||||
| Cohort interaction | 100 | 6.5 | 100 | 29.0 | 88.0 | 40.0 | 92.5 | 96.0 |
| CAP | 100 | 4.0 | 100 | 26.5 | 100 | 44.5 | 69.0 | 69.0 |
| cagLASSO | 100 | 1.5 | 100 | 19.0 | 99.5 | 23.5 | 76.5 | 75.5 |
| Different cohort sizes and different disease rates | ||||||||
| Cohort interaction | 100 | 6.5 | 100 | 23.0 | 71.5 | 31.5 | 78.5 | 82.5 |
| CAP | 100 | 4.0 | 100 | 18.0 | 97.5 | 38.0 | 64.0 | 64.0 |
| cagLASSO | 100 | 1.5 | 100 | 15.0 | 93.0 | 23.0 | 75.0 | 72.5 |
“Cohort interaction” refers to the pooled analysis using the interaction terms of covariates with cohort-specific membership indicators; “CAP” refers to the composite absolute penalty method; “cagLASSO” refers to the composite adaptive group LASSO penalty method; “Ave.” refers to the average effect of the covariate and its true value is listed below in the parenthesis; “Hetero.” refers to the heterogeneous effects of the covariate and the true values are listed below in the parenthesis.
