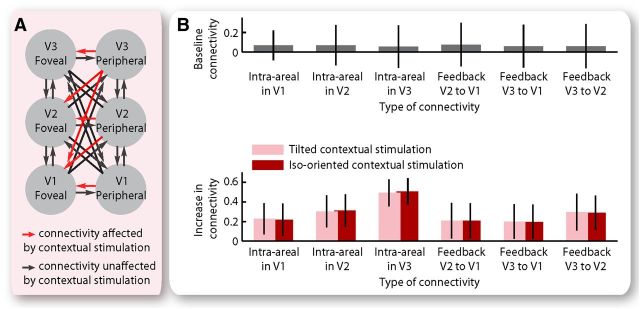
Figure 4.
Contextual modulation of cortical effective connectivity. A, The results from Bayesian model comparison suggested contextual modulation of intra-areal and feedback connectivity from peripheral to foveal retinotopic regions, but not of other intra-areal or interareal connectivity between foveal and peripheral retinotopic regions. B, At the baseline condition where either a blank screen or an isolated central grating or an isolated surrounding grating was presented, the intra-areal and feedback connectivity from peripheral to foveal retinotopic regions was not significantly different from zero. Under contextual stimulation, a significant increase was observed in intra-areal and feedback connectivity from peripheral to foveal retinotopic regions, regardless of whether the surrounding and the central gratings had different or identical orientation. Bar chart represents the mean and 95% confidence interval of the maximum a posteriori estimates across participants (N = 20).