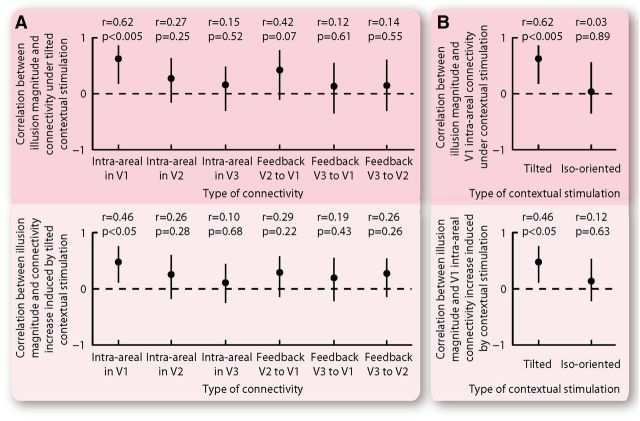
Figure 6.
Specificity of correlation between cortical effective connectivity and tilt illusion magnitude. A, Contextual stimulation affected intra-areal connectivity within each retinotopic visual cortex from its peripheral to its foveal region, and feedback connectivity between different retinotopic visual cortices from the higher peripheral to the lower foveal region. For each of these affected connectivities, we calculated its interindividual correlation with the tilt illusion magnitude. The correlation was significant only for intra-areal connectivity within V1. B, Contextual stimulation affected cortical effective connectivity regardless of whether the surrounding context had a different and an identical orientation as the central stimulus. For each of these two stimulation conditions, we calculated the interindividual correlation between cortical effective connectivity and tilt illusion magnitude. The correlation was significant for the tilted contextual stimulation but not for the iso-oriented contextual stimulation. The statistical values represent Spearman's ρ and its bootstrap confidence interval with FDR correction for multiple comparisons (α = 0.025).