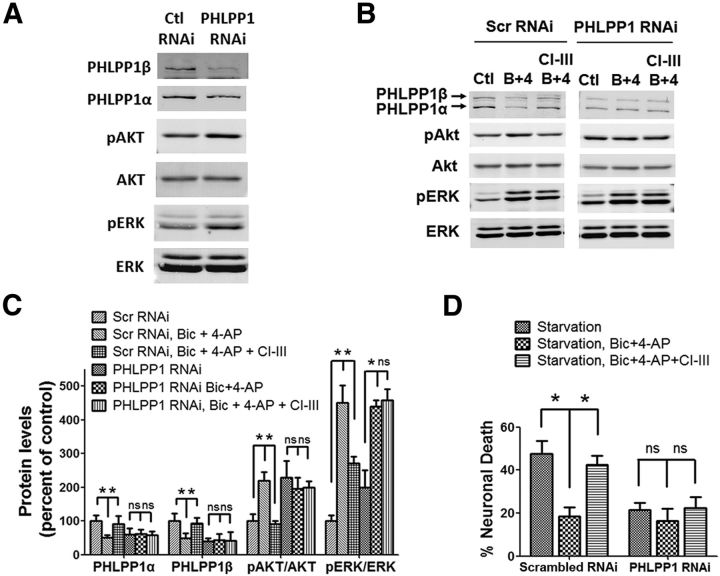
Figure 3.
Lentiviral shRNA knockdown of PHLPP1 mimics the neuroprotective effect of synaptic NMDAR activation and eliminates the effect of calpain inhibition on neuroprotection. A, Cultured cortical neurons were infected by PHLPP1 shRNA lentivirus or scrambled shRNA lentivirus. The levels of indicated proteins in infected neurons were assessed by Western blot. B, shRNA lentivirus-infected neurons were treated with Bic and 4-AP or with CI-III, Bic, and 4-AP for 30 min. The levels of indicated proteins were assessed by Western blot. C, Quantitative analysis of Western blots similar to those shown in A and B. Bic and 4-AP treatment reduced PHLPP1α and PHLPP1β levels and increased p-Akt/Akt levels in scrambled RNAi-infected neurons but not in PHLPP1 RNAi-infected neurons. CI-III blocked Bic and 4-AP-induced changes in PHLPP1, p-Akt/Akt, and p-ERK/ERK levels in scrambled RNAi-infected neurons but not in PHLPP1 RNAi-infected neurons. *p < 0.05; ns, not significantly different; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test; n = 3. Error bars indicate SEM. D, shRNA lentivirus-infected neurons were subjected to starvation for 3 d. PHLPP1 RNAi-infected neurons showed decreased neuronal death compared with scrambled RNAi-infected neurons. Bic and 4-AP incubation along with starvation decreased neuronal death in scrambled RNAi-infected neurons but not in PHLPP1 RNAi-infected neurons. CI-III blocked Bic and 4-AP induced reduction of neuronal death in scrambled RNAi-infected neurons but not in PHLPP1 RNAi-infected neurons. Approximately 300–500 cells were counted for each group in each independent experiment. *p < 0.05; ns, not significantly different; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test. n = 3. Error bar indicates SEM.