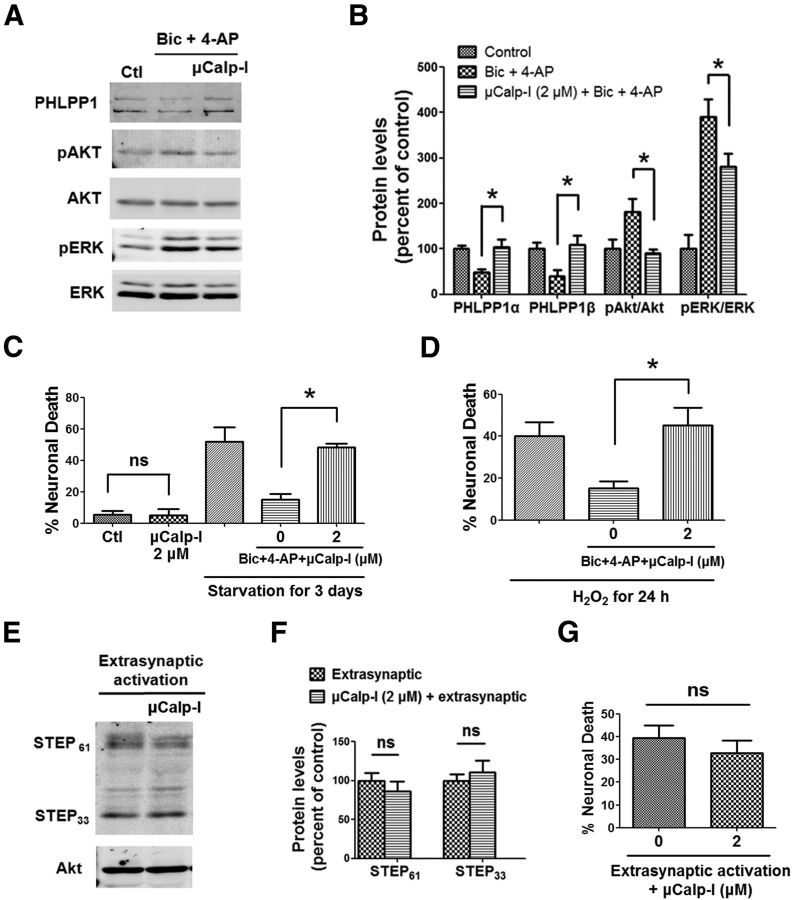
Figure 6.
A μ-calpain-specific inhibitor blocks synaptic NMDAR-induced neuroprotection but not extrasynaptic NMDAR-induced neurotoxicity. A, Cortical neurons were treated with 20 μm Bic and 100 μm 4-AP for 30 min and lysed for Western blot. In another group, 2 μm μCalp-I was applied 10 min before Bic and 4-AP treatment. The levels of indicated proteins were assessed by Western blot. B, Quantitative analysis of Western blots similar to those shown in A. μCalp-I (2 μm) blocked Bic- and 4-AP-induced changes in PHLPP1, pAkt/Akt, and pERK/ERK levels. *p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test; n = 3. Error bars indicate SEM. C, μCalp-I (2 μm) blocked Bic- and 4-AP-induced neuroprotection against starvation in cortical neurons. Incubation of neurons with 2 μm μCalp-I alone for 3 d did not cause cell death. At least 300–500 Hoechst-stained cells were counted for each group in each independent experiment. *p < 0.05; ns, not significantly different; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test. n = 3–5. Error bar indicates SEM. D, μCalp-I (2 μm) blocked Bic- and 4-AP-induced neuroprotection against H2O2. n = 3. E, Cortical neurons were treated with the protocol for extrasynaptic NMDAR activation and then lysed for Western blot. In another group, 2 μm μCalp-I was applied 10 min before extrasynaptic NMDAR activation. F, Quantitative analysis of Western blots similar to those shown in E. μCalp-I (2 μm) did not affect STEP degradation induced by extrasynaptic NMDAR activation (ns, not significantly different; two-tailed t test; n = 3). Error bars indicate SEM. G, μCalp-I (2 μm) did not affect neuronal death induced by extrasynaptic NMDAR activation. Approximately 300–500 Hoechst-stained cells were counted for each group in each independent experiment. ns, not significantly different; two-tailed t test; n = 4–5. Error bar indicates SEM.