Figure 1.
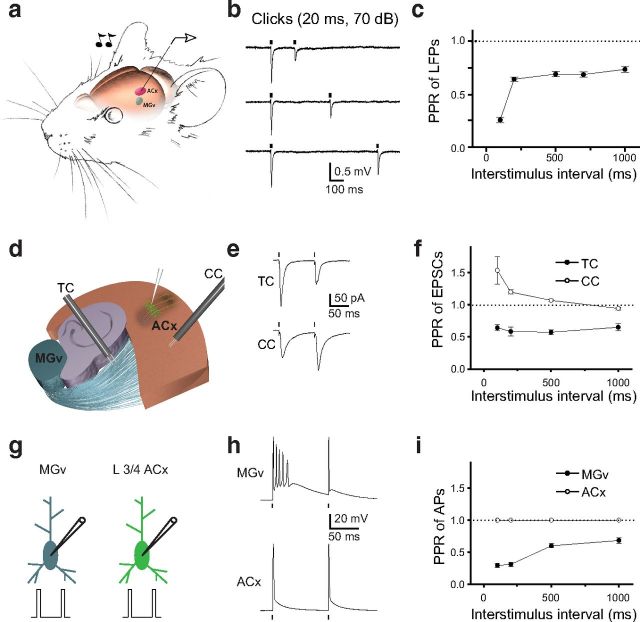
Forward suppression of sound-evoked responses in the ACx and PPD at TC synapses. a, Illustration of the experimental setup in which a pair of clicks (20 ms, 70 dB) was delivered to the contralateral ear of a mouse. LFPs were recorded from L3/4 of the ACx. The MGv is shown in blue, and the ACx is shown in red. b, LFP traces (average of 10–15 sweeps) in response to pairs of clicks delivered at 200, 400, and 700 ms ISIs. c, Mean PPR of LFPs (peak LFP2/peak LFP1) as a function of the ISI. d, A diagram of the TC slice containing portions of the MGv, hippocampus, and the ACx. L3/4 neurons in the ACx are shown in green. Stimulation electrodes (black) placed into the TR to stimulate TC projections and in the ACx to stimulate CC projections. e, Representative traces of TC PPD and CC PPF. f, Mean TC and CC PPR of EPSCs (EPSC2/EPSC1) as a function of ISI. g, Depiction of whole-cell recordings from thalamic relay neurons in the MGv and L3/4 pyramidal neurons in the ACx. Pairs of brief depolarization pulses (0.2 ms, 3–4 nA) are delivered to evoke APs in these cells. h, Representative voltage traces in MGv and ACx neurons in response to a pair of depolarization pulses. i, Mean PPR of APs (AP2/AP1) at different ISIs. Dots correspond to the delivery of clicks in vivo (b), stimulation of TC or CC projections (e), or depolarizing pulses (h) in slice experiments.