Figure 7.
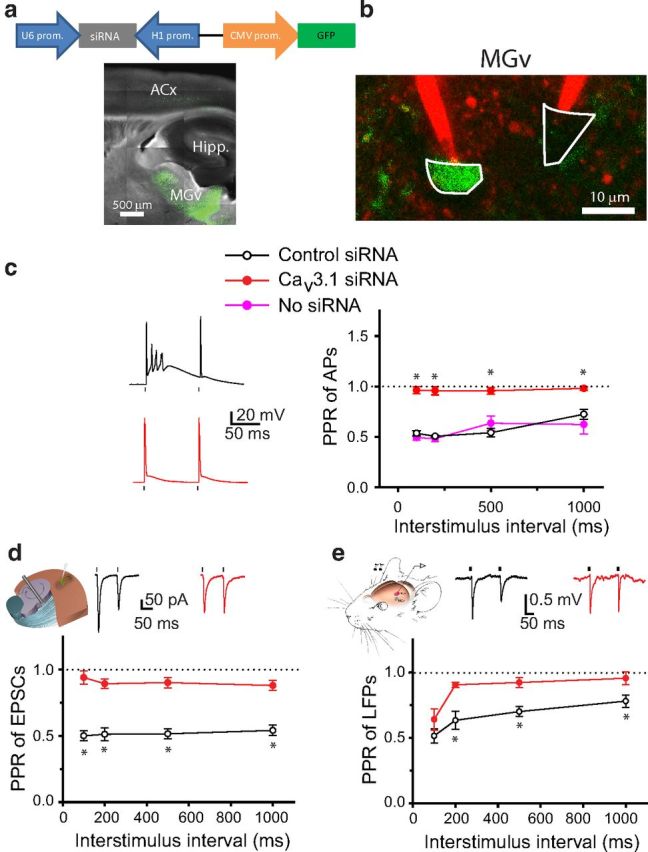
Knockdown of Cav3.1 T-type calcium channels in MGv neurons reduces TC PPD and forward suppression of sound-evoked responses in the ACx. a, Diagram of a lentivirus encoding Cav3.1 siRNA and GFP (top). Representative image of a TC slice from a mouse injected with Cav3.1 siRNA into the MGv (bottom). b, Image of GFP-positive (infected with siRNA lentivirus, green) and GFP-negative (not infected, black) MGv neurons that are targeted with two glass pipettes filled with Alexa Fluor 594 (red). c, Representative voltage traces (left) and average PPR of APs as a function of ISI recorded in MGv neurons either not infected or infected with viruses containing control siRNA or Cav3.1 siRNA (right). d, Mean PPR of EPSCs recorded in slices from mice injected with control siRNA or Cav3.1 siRNA into the MGv. Inset shows representative EPSP traces in response to a pair of stimuli. e, Mean PPR of LFPs recorded in the ACx in vivo in mice injected with control siRNA or Cav3.1 siRNA into the MGv. Inset shows representative LFP traces in response to a pair of clicks. c–e, Dots above or below the traces represent the delivery of depolarizing pulses to cell bodies of MGv neurons (c), stimuli to the TR (d), or clicks to the contralateral ear (e). *p < 0.01.
