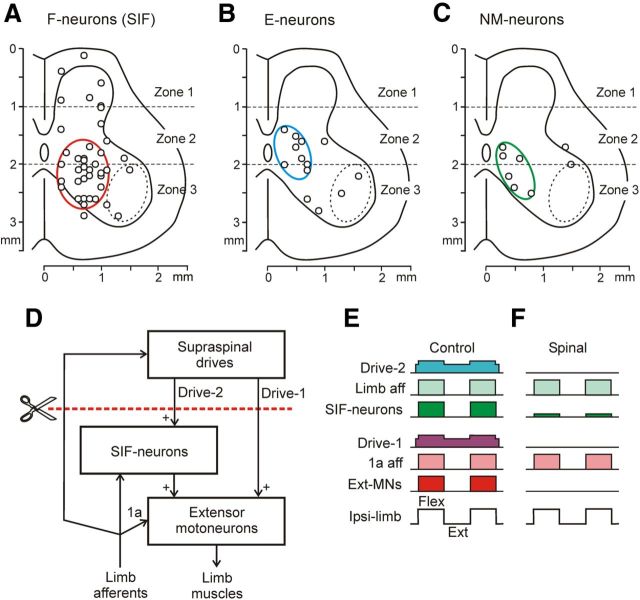
Figure 9.
A-C, Location of strongly inactivated neurons (>80% decrease of frequency) in different groups: F-neurons (A), E-neurons (B), and NM-neurons (C), on the cross section of the spinal cord. Areas with high density of these neurons are demarcated by red, blue, and green ellipses, respectively. D–F, Presumed neuronal mechanisms underlying the disappearance of PLRs during spinal shock. D, Principal components of PLR mechanisms. E,F, Activity of these components in the nonspinalized (E) and spinalized (F) animals subjected to periodical platform tilts causing flexion/extension limb movements. SIF-neurons are the strongly inactivated F-neurons; the red interrupted line shows the level of spinalization. See text for explanations.