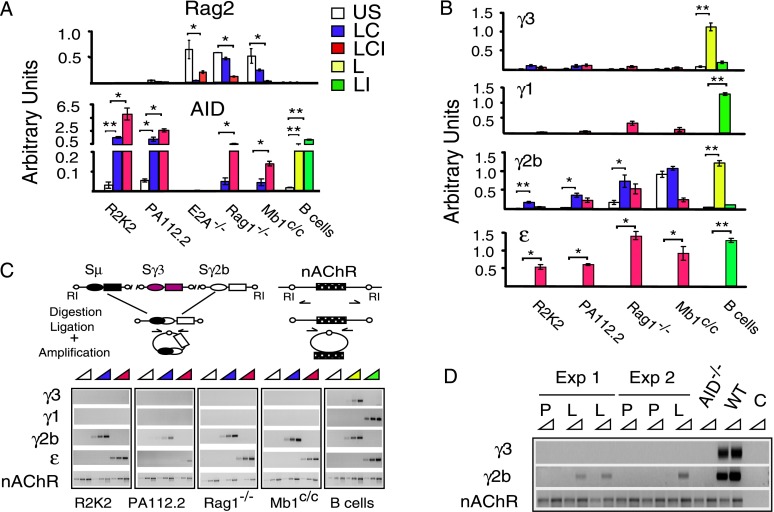
Figure 1.
Pro-B cells undergo inducible CSR. E2A-deficient pre-pro-B cells, Rag1-deficient or Mb1-deficient pro-B cells, Abelson transformed pro-B-cell lines (R2K2), and pre-B-cell lines (PA112.2) were unstimulated (US) or activated with LPS+CD40L (LC) or LPS+CD40L+IL4 (LCI), and wild-type (WT) resting splenic B cells were unstimulated or activated with LPS (L) or LPS+IL4 (LI). (*) P ≤ 0.05; (**) P ≤ 0.001–0.0001. (A,B) Quantitative RT–PCR assays for Rag2 and AID (A) and GLTs γ3, γ1, γ2b, and ɛ (B) from five samples from three to five independent experiments were normalized to the rRNA 18S transcript. (C, top) DC-PCR assay schematic, EcoRI (RI) sites, and nAChR gene loading control. (Bottom) DC-PCR analyses of μ → γ3, μ → γ1, μ → γ2b, and μ → ɛ CSR are representative of three independent experiments. (D) DC-PCR analysis of pro-B cells from Rag1−/− mice injected with LPS or PBS. Wild-type or AID−/− splenic B cells activated with LPS or no template control (C) are representative of three independent experiments.