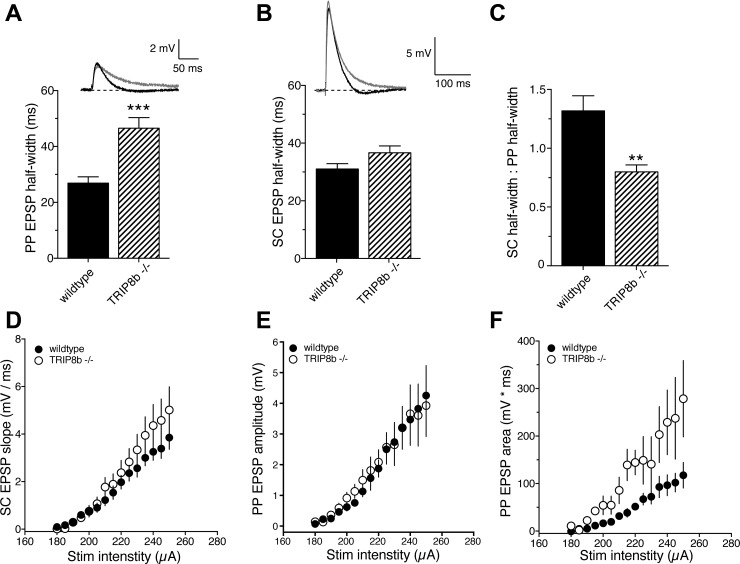
Fig. 1.
TRIP8b deletion preferentially affects perforant path (PP) excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs). A: PP EPSP half-width was significantly greater in TRIP8b−/− neurons compared with wild-type neurons. B: Schaffer collateral (SC) EPSP half-width was not significantly different between wild-type and TRIP8b−/− neurons. C: the ratio of SC to PP EPSP half-width was significantly smaller in TRIP8b−/− neurons. D: relationship between SC EPSP slope and stimulus intensity for wild-type and TRIP8b−/− neurons. E and F: amplitude (E) and area (F) of PP EPSPs as a function of stimulus intensity. **P < 0.01 vs. wild type; ***P < 0.005 vs. wild type.