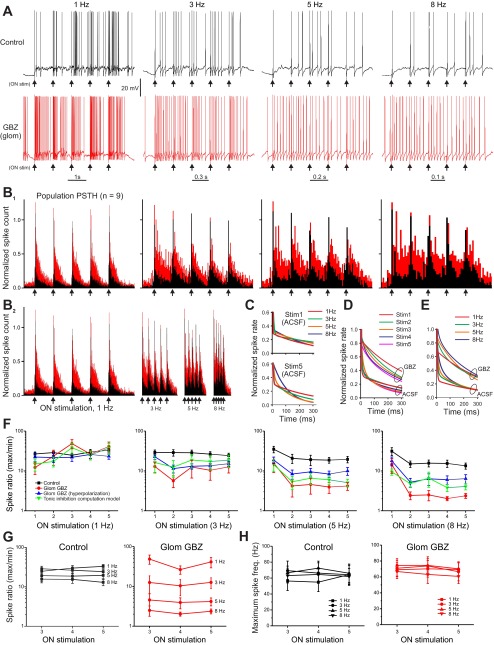
Fig. 2.
Intraglomerular inhibition reduces MC spike responses to ON stimulation at input frequencies >3 Hz. A: current-clamp recording of ON evoked spikes in a MC in aCSF (black) and following restricted glomerular GBZ application (red). Note, the x-axis scale in each panel is different to maintain stimulation spacing constant. B1 and B2: population peristimulus time histograms (PSTH) of MC spike count following ON stimulation at 1, 3, 5, and 8 Hz (arrows, n = 8 cells) in aCSF (black) superimposed on the spike PSTH following glomerular restricted application of 100 μM GBZ (red). Glomerular injection of 100 μM GBZ dramatically increases spike output. Note, the x-axis time scale in B1 vary to maintain constant stimulation spacing, B2 shows the same PSTH with a fixed time scale. C: curve fitting of the population MC spiking decay following stimulation 1 (top trace) and stimulation 5 (bottom trace) at 1, 3, 5, and 8 Hz. D: curve fitting of the population MC spiking decay in aCSF and glomerular injection of GBZ showing average for stimulations 1–5 showing the major slowing of decay rate with GBZ. E: curve fitting of the population MC spiking decay in aCSF and glomerular injection of GBZ averaged for frequencies 1, 3, 5, and 8 Hz. In aCSF or GBZ there is a slight slowing of decay rate at higher frequencies. F: ratio of maximum/minimum spike counts at each frequency. aCSF (black, n = 16 cells); Glom GBZ: restricted glomerular gabazine application (red, n = 8 cells); Glom GBZ (hyperpolarization): restricted glomerular gabazine application on hyperpolarized MTCs (blue, n = 8 cells) and computation model of tonic inhibition (green, n = 8 cells). G: population mean of the ratio between maximum and minimum spiking at each stimulation frequency in aCSF (left) and following GBZ (right) for steady-state responses from the 3rd to 5th stimulations in the ON stimulation train. Blocking interglomerular inhibition with GBZ decreases the max/min ratio as input frequency increases. H: population mean of the maximum spike frequency in each stimulation frequency in aCSF (left) and following GBZ (right) shows no significant differences in maximum spiking across frequencies.