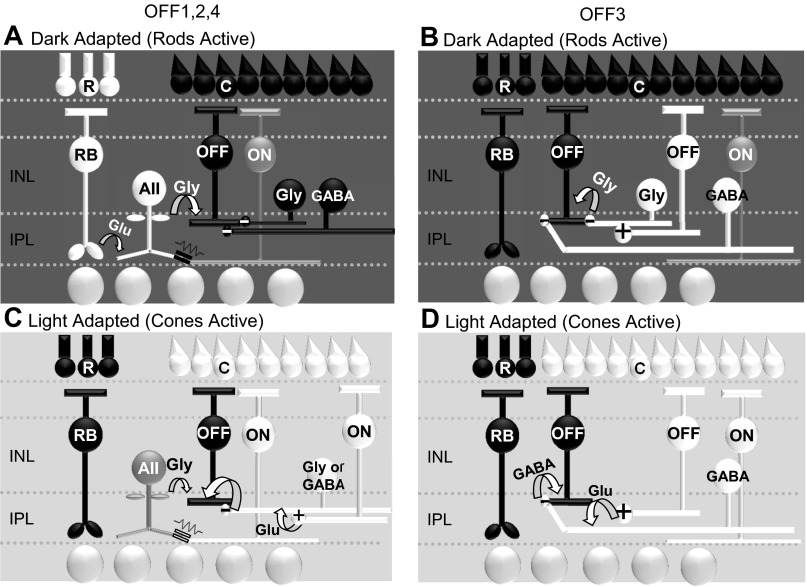
Fig. 9.
Summary schematics showing inhibitory input to OFF1,2,4 and OFF3 BCs under dark- and light-adapted conditions. A: under dark-adapted conditions, OFF1,2,4 BCs receive large light-evoked glycinergic inhibition from the rod-AII AC pathway in addition to other glycinergic and GABAergic inputs. This is done through crossover inhibition via excitation of the AII AC with dim light and serves as an ON inhibitory signal to the OFF pathway. B: under dark-adapted conditions, OFF3 BCs receive large light-evoked glycinergic and GABAergic inhibition from OFF cone pathways activated by brighter light intensities. C: under light-adapted conditions OFF1,2,4 BCs receive compensatory GABAergic and glycinergic inhibition from cone-activated ACs. The AII AC may receive depolarizing signals through gap junction connections with ON BCs and partly mediate inhibitory currents in the OFF1,2,4 BCs (Fig. 1, E and F). However, there is an overall higher proportion of GABAergic input in the light. D: in light-adapted conditions, OFF3 BCs receive compensatory inhibition solely mediated by GABAergic input from OFF cone-activated ACs.