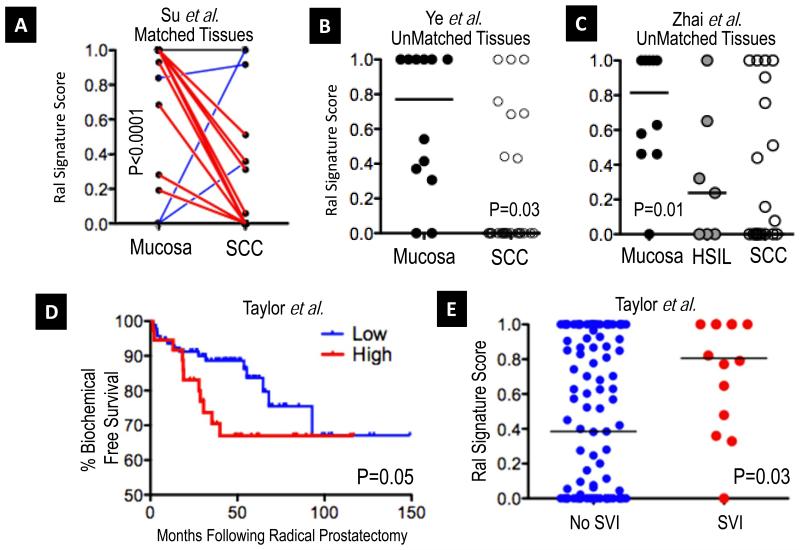
Figure 4. Ral Transcriptional Signature scores in squamous malignancy.
A. Using data from a published cohort of 53 patient-matched esophageal squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and adjacent normal mucosae (35), we observed a significant trend toward lower Ral signature score in cancer (P<0.0001, Wilcoxon matched pairs test). Plot shows matched pairs of mucosa and cancer, with decreases in signature score plotted red (N=37), similar scores plotted black (N=13) and increased scores plotted blue (N=3). B. In a second, unmatched cohort of 12 mucosae and 26 oropharyngeal SCCs (36), a similar pattern was identified (Mann-Whitney test, signature scores plotted and medians per group indicated, black lines) that was significant. C. In a third cohort of SCCs of the uterine cervix (N=21), high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL, (N=7), and normal cervical mucosae (N=10), we observed significantly lower scores in the neoplastic tissues as compared to the mucosae (Mann-Whitney test, Mucose vs. HSIL & SCC; scores plotted as in B), with biologically intermediate HSIL lesions showing scores between those of normal mucosae and SCC. The Ral Transcriptional Signature score and prostate cancer disease aggression. D. Using data from a recently published cohort (N=131) of prostatic adenocarcinomas from Taylor et al. (40) we found that Ral signature scores could significantly stratify biochemical recurrence free survival. (Kaplan-Meier plot, Ral signature classes plotted at optimal discriminating point for survival, Log Rank Test). E. In the Taylor et al. cohort, a significant difference was observed between cases that did or did not evince seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) at prostatectomy (Mann-Whitney test, signature scores plotted and medians indicated per group, black lines).