Figure 4.
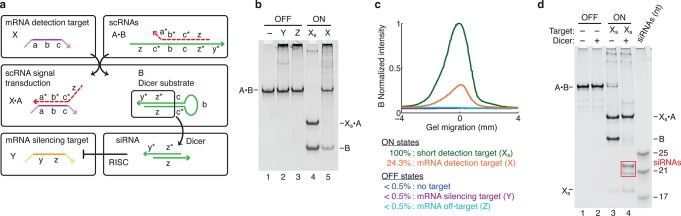
Conditional shRNA formation using a single stable scRNA. (a) Mechanism 3. scRNA A·B detects mRNA detection target X (containing subsequence ‘a-b-c’), leading to production of shRNA Dicer substrate B targeting mRNA silencing target Y (containing independent subsequence ‘y-z’). scRNA A·B is stable in the absence of X. X partially displaces A from B via toehold-mediated 3-way branch migration, exposing a previously sequestered internal toehold, ‘c’, within B, mediating a further 3-way branch migration that disassembles B from X·A to yield shRNA Dicer substrate B. Domain lengths: |a| = 12, |b| = 14, |c| = 3, |y| = 2, |z| = 19. Chemical modifications (2′OMe-RNA): A (dashed backbone). (b) Conditional Dicer substrate formation. OFF state: minimal production of Dicer substrate B in the absence of detection target X, the presence of mRNA silencing target Y, or the presence of mRNA off-target Z. ON state: strong production of B in the presence of short RNA detection target Xs (‘a-b-c’) or full-length mRNA detection target X. (c) Quantification of the Dicer substrate band (B) in panel (b). (d) Conditional Dicer processing. OFF state: minimal processing of the reactants (lane 2). ON state: efficient processing of shRNA Dicer substrate B (lane 4), yielding canonical 21- and 22-nt siRNAs (boxed bands). See Section S4 for additional computational and experimental studies of Mechanism 3.
