Figure 6.
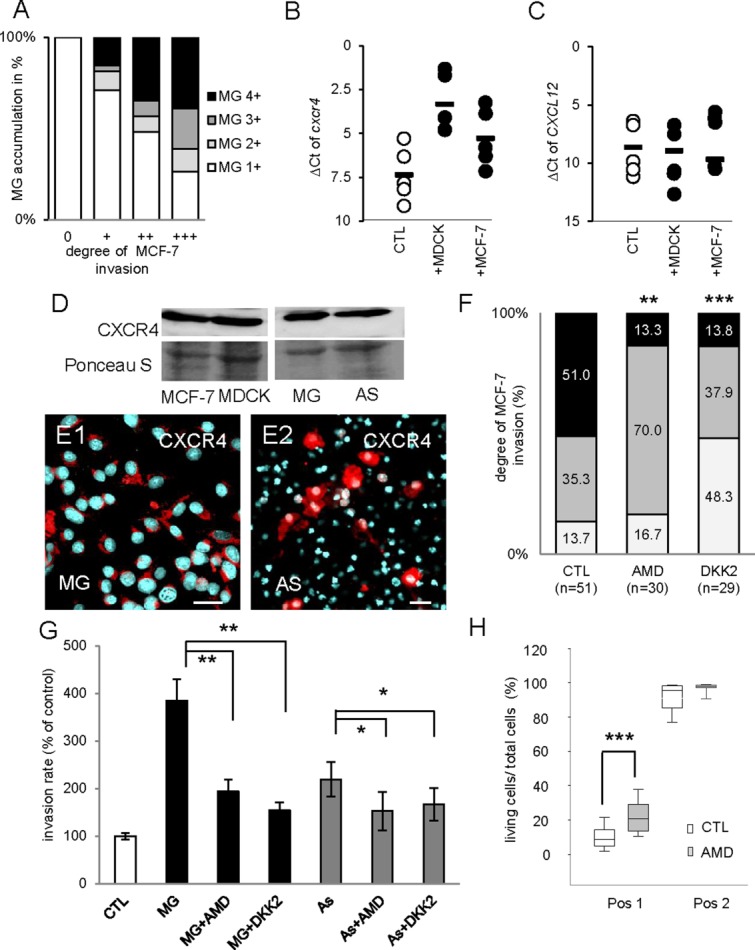
CXCR4 and WNT signaling are involved in microglia- and astrocyte-induced invasion. (A) The degree of MCF-7 invasion and microglia (MG) accumulation at the contact area/invasion front was determined in brain slice cocultures (n = 203). The analysis revealed a significant correlation between the degree of tumor invasion and the degree of microglial accumulation (Spearman’s test; P < 0.001). (B and C) qRT-PCR results of cxcr4 and cxcl12 illustrated by the ΔCt method. Coculture with MDCK or MCF-7 cells for 96 h upregulates cxcr4 but not its ligand, cxcl12 in the organotypic brain slices. Line represents the mean value of all experiments and each dot represents the mean value of triplicate analyses with n ≥ 15 from three individual experiments. (D) MDCK, MCF-7, microglia, and astrocytes (AS) express CXCR4 protein detected by immunoblot. (E1 and E2) The glial cells astrocytes and microglia reveal a heterogeneous expression pattern of CXCR4 (red) on immunofluorescence staining counterstained with DAPI (scale bars represent 20 µm). (F) The invasion of the MCF-7-GFP cells into the whole brain slice was significantly reduced after DKK2 as well as AMD3100 treatment. (G) The influence of indirect cocultures with microglia or astrocytes on carcinoma cell invasion measured by modified Boyden chamber assays. Treatment with WNT inhibitor DKK2 as well as CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100 significantly reduced both the astrocyte- or microglia-induced carcinoma cell invasion. Data represent mean ± SEM with n ≥ 9 of three individual experiments. (H) The CXCR4 inhibitor also partially rescued the glial-induced apoptosis of MDCK at Position 1 (scheme see Fig. 4A) similar to clodronate or DKK2 treatment shown in Fig. 5C. Data represent mean ± SEM with n ≥ 9 from more than three individual experiments. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
