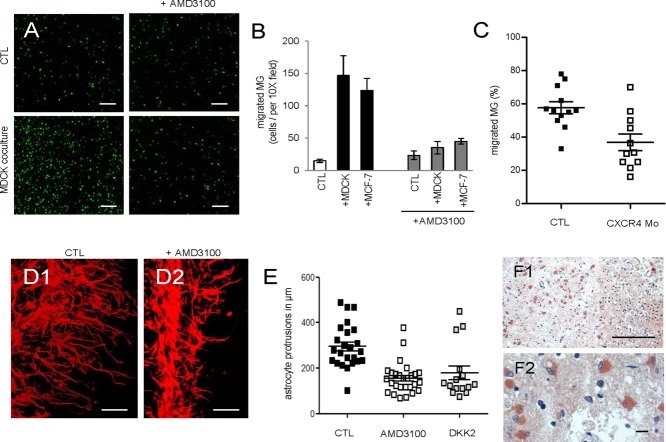
Figure 8.
CXCR4 knockdown/ inhibition affects microglial and astrocytic damage response. (A and B) Results of the microglia chemotaxis assays toward MDCK and MCF-7 cells. Both cocultures significantly enhanced microglia migration. (A) Representative microglial images were shown ± MDCK coculture and ± treatment with the CXCR4 inhibitor (AMD 3100, 1 µg/mL). AMD3100 reduced the enhanced microglial migration toward MDCK almost to CTL level (scale bars represent 200 µm). (B) Results demonstrate migrated microglial cells per 10× field, data represent mean ± SEM; n = 40. (C) Knockdown effects of CXCR4 in zebrafish larvae: Percentage of microglia in the optic tectum moving to the injury site in CTL (n = 12) and CXCR4-morpholino (CXCR4-Mo) injected embryos (n = 11) were measured. The CXCR4-Mo significantly reduced the microglial migration toward the injury site (line = mean and SEM, P = 0.004). (D and E) Cocultured with 3D-MCF-7-GFP for 96 h ± 1 µg/mL of AMD3100 were stained with anti-GFAP-TRITC (red). The length of the astrocyte protrusions were reduced after AMD3100 (P < 0.001) or DKK2 (P = 0.009) treatment (scale bars represent 100 µm); line = mean and SEM (n ≥ 15). (F) Protein expression of CXCR4 in human stroke samples using IHC (scale bar represents 20 µm, in the upper panel 200 µm). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]