Figure 1.
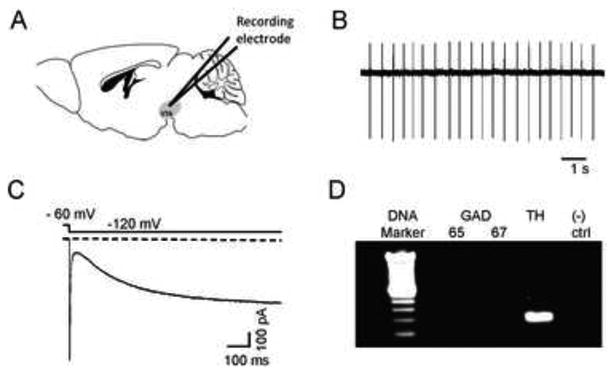
Characteristics of DAergic neurons in VTA sagittal slices. Illustration of a mouse sagittal section containing the VTA (shaded region). B) Representative cell-attached recording from a putative DAergic neuron. DAergic neurons had characteristic low baseline firing frequencies (1-5 Hz) and as shown in C), expressed the hyperpolarizing activated cation current, Ih. Currents were elicited by a hyperpolarizing step from a holding potential of -60 mV to -120 mV as indicated. D) At the end of each recording, the content of each neuron was aspirated into the patch pipette and TH expression was verified by single-cell real-time PCR. A representative DNA agarose gel is shown illustrating a typical result for a DAergic neuron. Only neurons that clearly expressed TH and not GAD 65/67 were included in the analysis. As a negative control for the PCR, a sample containing no RNA was used (“(-) ctrl”).
