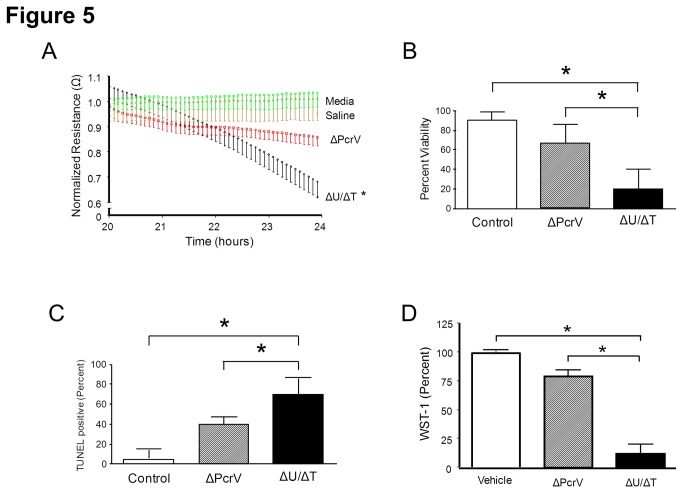
Figure 5. P. aeruginosa T3SS needle tip complex protein PcrV increases PMVEC permeability associated with cell damage during late phase infection.
A. Isolated rat PMVECs were grown on gold electrodes to confluence and resistance across the monolayer determined using an ECIS system. PMVECs were inoculated with medium alone, saline solution (vehicle control), or with either P. aeruginosa mutant at a 40:1 MOI. Inoculation with PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) caused significant increases in PMVEC permeability (i.e., decreased electrical resistance) compared to no treatment (medium alone), vehicle control inoculation, or inoculation with PA103 (ΔPcrV). The average numbers of resistance recordings from at least 6 independent experiments per condition are presented. Error bars are the standard error of the mean. The asterisk indicates that PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) was significantly different compared to all other conditions (P < 0.05) by one-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post-hoc test. B. Isolated rat PMVECs were grown in culture dishes to confluence and viability assessed by Trypan Blue exclusion assay. PMVECs were inoculated with saline solution (vehicle control), or with either P. aeruginosa mutant at a 40:1 MOI. PMVEC viability was assessed at 24-hours post-inoculation, and data are expressed as percent total viable cells. Inoculation with PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) significantly increased PMVEC death compared to vehicle control inoculation and PA103 (ΔPcrV). The average viable PMVEC numbers from at least 10 independent experiments per condition are presented. Error bars are the standard error of the mean. The asterisks indicate that PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) was significantly different compared to all other conditions (P < 0.05) by one-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post-hoc test. C. Isolated rat PMVECs were grown on glass cover slips to confluence and cell death assessed by TUNEL staining. PMVECs were inoculated with saline solution (vehicle control), or with either P. aeruginosa mutant at a 40:1 MOI. PMVEC death was assessed at 24-hours post-inoculation, and numbers of dead cells are expressed as a percent of the total number of cells. Inoculation with PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) significantly increased PMVEC death compared to vehicle control inoculation and PA103 (ΔPcrV). Error bars are the standard error of the mean from 3 independent experiments. The asterisks indicate that PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) was significantly different compared to all other conditions (P < 0.05) by one-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post-hoc test. D. Isolated rat PMVECs were grown in culture dishes to confluence and cellular fitness assessed by WST-1 metabolism assay. PMVECs were inoculated with saline solution (vehicle control), or with either P. aeruginosa mutant at a 40:1 MOI. PMVECs were assessed at 24-hours post-exposure for each condition, and data are expressed as percent of the vehicle control. Infection with PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) significantly decreased PMVEC fitness compared to vehicle control inoculation and PA103 (ΔPcrV). The average amount of WST-1 metabolism from at least 5 independent experiments per condition is presented. Error bars are the standard error of the mean. The asterisks indicate that PA103 (ΔU/ΔT) was significantly different compared to all other conditions (P < 0.05) by one-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls post-hoc test.