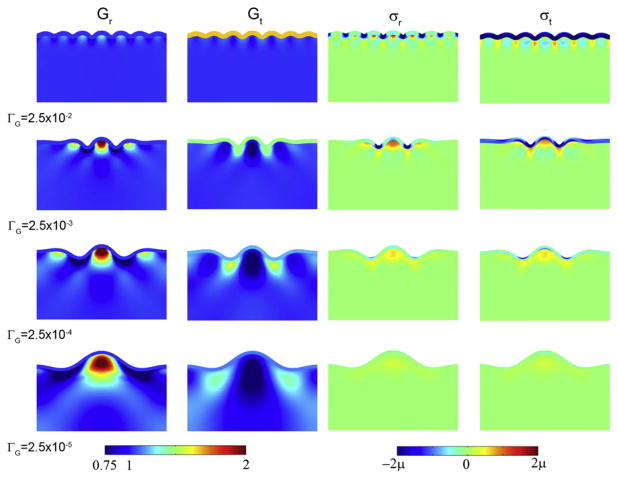
Fig. 11.
Effects of cortical growth rate on wavelength, subcortical growth, and stress in a 2-D model of cortical folding. In this model folding is driven by tangential growth of a single outer layer, accompanied by stress-driven radial and tangential growth in the foundation (Bayly et al., 2013). The elastic shear modulus is the same in both regions. Each column contains spatial maps of a different variable superimposed on the deformed geometry: radial growth Gr; tangential growth Gt; radial stress σr; tangential stress σt. Each row corresponds to a different scaled cortical growth rate. (Row 1)Relative growth rate ΓG = 2.5 × 10−2, at scaled time τ=0.060; (Row 2) ΓG = 2.5 × 10−3, at τ=0.035; (Row 3) ΓG = 2.5 × 10−4, at τ=0.014; (Row 4) τ = 2.5 × 10−5, at τ =0.08. Reproduced with permission from Bayly et al. (2013).