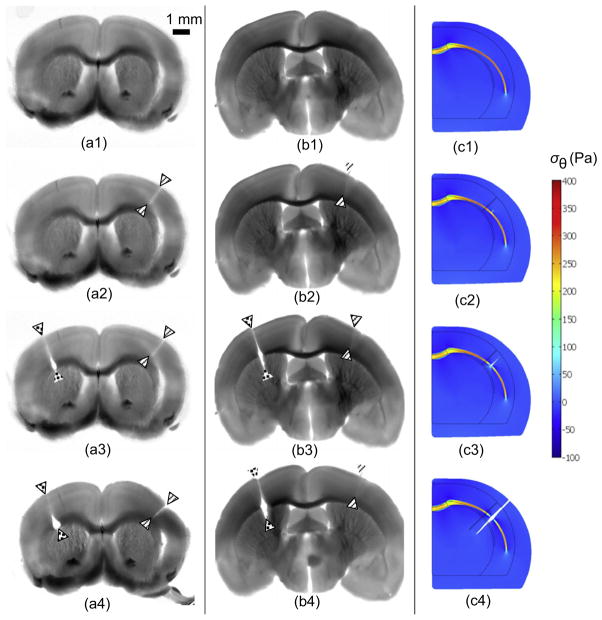
Fig. 6.
Micro-dissection study of stress in a coronal slice of an adult mouse brain. (a1, b1) Brain section before dissection (1 mm thick, obtained by vibratome immediately after sacrifice). (a2, b2) One radial cut (solid arrowheads) was made only through the cortical gray matter, and did not open. (a3, b3) A second radial cut (open arrowheads) was made through the underlying white matter (a3) or into the interior gray matter (b3). The cut opened at the site of the white matter tract. (a4, b4). (c1–c4) Normalized circumferential stress ( ) distribution in finite element models of the dissection experiments (μ*=0.5, ). Following imposed growth, gray matter is in compression and white matter is in tension. Simulated radial cuts were made into cortical gray matter (c2), white matter (c3), or deep gray matter (c4), respectively. Reproduced with permission from Xu et al. (2009).