Figure 1.
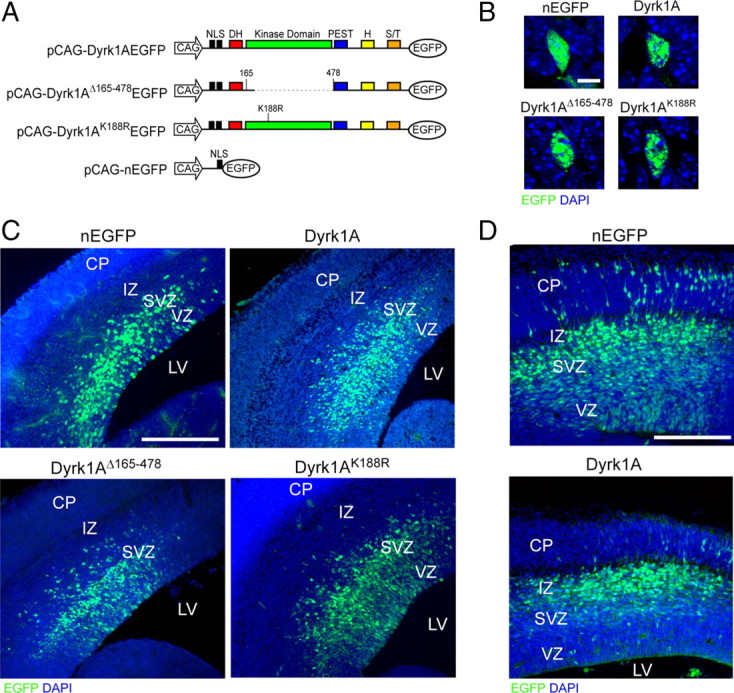
In utero electroporation of Dyrk1A–EGFP constructs in the mouse neocortex. A, Diagram of the plasmids used for IUE. All constructs contained the CAG hybrid promoter, an NLS, and the EGFP reporter fused in-frame to Dyrk1A coding sequences. Expression constructs encode wild-type Dyrk1A (pCAG–Dyrk1AEGFP), a kinase domain deletion (pCAG–Dyrk1AΔ165-478EGFP), and a kinase mutation (pCAG–Dyrk1AK188REGFP). A construct encoding nuclear EGFP alone (pCAG–nEGFP) with an NLS was used as a control. H, Histidine repeat; S/T, serine/threonine-rich regions. B, Subcellular localization of Dyrk1A proteins in transfected neural cells. Confocal images of individual neural cells in the embryonic neocortex expressing Dyrk1A proteins or control nEGFP (green). All proteins accumulated in the nucleus as indicated by colocalization with DAPI (blue), but Dyrk1A proteins exhibited a speckle-like distribution pattern. C, Expression pattern of transfected cells 24 h after IUE. Coronal sections of the lateral neocortex were obtained and imaged by direct EGFP fluorescence (green) and DAPI counterstain (blue) using confocal microscopy. Cells expressing nEGFP as well as Dyrk1AK188R and Dyrk1AΔ165-478 appeared to be widely distributed in the VZ, SVZ, and IZ. Dyrk1A+ cells were primarily excluded from the VZ. D, Expression of transfected cells 48 h after IUE. Representative images of the neocortex were obtained as above, showing that Dyrk1A+ cells were preferentially excluded from the VZ. Scale bars: B, 5 μm; C, D, 500 μm. LV, Lateral ventricle; CP, cortical plate.
