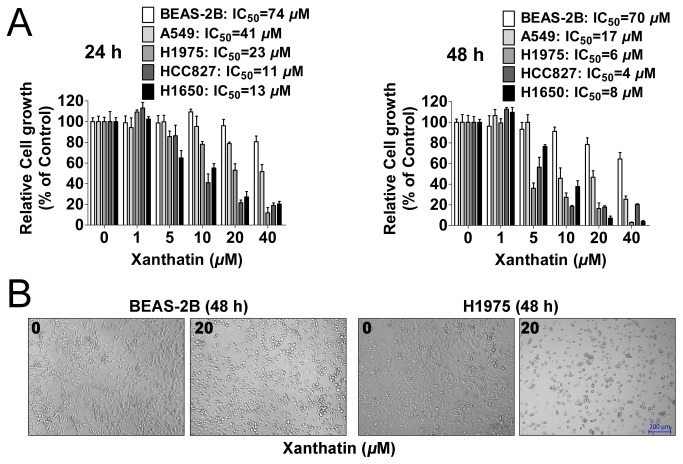
Figure 1. In vitro treatment of human NSCLCs with xanthatin inhibits the proliferation potential in a dose- and time-dependent manner.
(A) NSCLCs (A549, H1975, HCC827, H1650 cells) and human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) were exposed to indicated concentrations of xanthatin (1, 5, 10, 20, 40 μM) for 24 h and 48 h, respectively. Cell viability was determined by One solution cell proliferation assay. The data are presented as mean ± SD. The values are expressed as percentage of viable cells normalized to percentage of viable cells in 0.5% DMSO-treated cells. The concentration of xanthatin resulting in 50% inhibition of control growth (IC50) was calculated by SPSS statistics software using Probit model. (B) Representative images of cell morphology in BEAS-2B and H1975 cells were taken after 48 h treatment with or without 20 μM xanthatin (100×, scale bar represents 200 μm).